Advanced Threat Protection: A Real-Time Threat Killer Machine
Traditional security solutions like firewalls and legacy antivirus are not effective against advanced threats like zero-day vulnerabilities and advanced persistent threat (APT) attacks. Advanced threats require advanced threat protection, which focuses on real-time response. Advanced threat protection solutions leverage UEBA and AI to reduce false positives and ensure swift and active protection against data breaches.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about machine learning.
What Is Advanced Threat Protection?
Advanced threat protection (ATP) is a set of practices and solutions that you can use to detect and prevent advanced malware or attacks. Generally, ATP solutions include a combination of network devices, malware protection systems, email gateways, endpoint agents, and a centralized management dashboard. You can include solutions as software or as managed services.
If you want to learn about detection, check out our guide about advanced threat detection.
Why You Need Advanced Threat Protection
Traditional security tooling, such as antivirus and firewalls, relies on signature-based matching of known malware or blacklisting of known threat sources. However, these measures can no longer stop many cyber attacks. Modern attacks use a variety of dynamic attack vectors and methods that can bypass traditional methods.
Advanced threat protection solutions can detect these attacks and adapt protections to stop attacks. These solutions proactively monitor systems to identify possible threats, eliminate attackers, and alert security teams to issues.
Benefits of ATP solutions include:
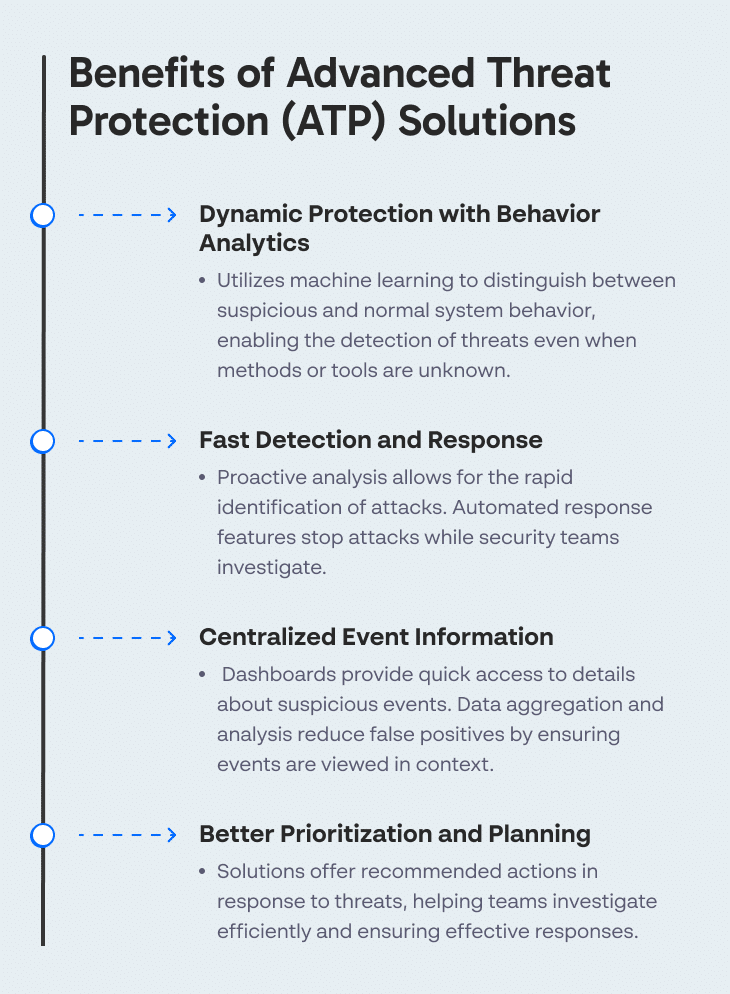
- Dynamic protection with behavior analytics—uses machine learning to differentiate suspicious from normal system behavior. This enables solutions to detect threats even if methods or tools are unknown.
- Fast detection and response—proactive analysis ensures that attacks are caught as quickly as possible. Automated response features ensure that attacks are stopped while security teams investigate. For more information about planning your incident response strategy, check out our guide about incident response plans.
- Centralized event information—dashboards help security analysts quickly access details about and respond to suspicious events. Aggregation of data and analyses helps reduce false positives by ensuring that events are viewed in context.
- Better prioritization and planning—solutions can provide recommended actions in response to threats. This helps teams investigate events efficiently and ensures that the most effective responses are taken.
Advanced threat protection solutions focus on real-time response. Solutions work through the lifecycle of an attack, creating more opportunities for detection. This means more attacks are stopped and faster responses enable you to minimize any damage caused and speed recovery time. Additionally, because attack data is correlated and aggregated, you can use solutions to develop and improve threat intelligence for even greater protection.
How Advanced Threat Protection Works
Advanced threat protection solutions focus on providing detection, protection, and response capabilities. These capabilities help ensure that:
- Attacks are stopped or mitigated before systems are damaged
- In-progress attacks are disrupted and eliminated as soon as possible
- Data from attacks, whether successful or not, is incorporated into future protection mechanisms
To accomplish these capabilities, solutions incorporate the following components:
- Real-time visibility—provided by continuous monitoring for real-time detection of threats and suspicious behaviors. Having continuous real-time visibility helps ensure that attacks are brief and cause minimal damage.
- Context—data surrounding security threats is aggregated, correlated, and made available to security solutions and teams. This helps ensure that alerts are relevant and enables teams to prioritize responses.
- Data awareness—incorporates system data, such as data priority, to evaluate threats and appropriate responses. Additionally, dashboards help ensure that security teams are aware of where data is and who is accessing it.
If you are using a managed ATP service, providers typically provide monitoring, analysis, and response. However, providers may pass along higher-level events or events dealing with high priority data to your in-house team for a more thorough analysis and response.
Tips From Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better adapt to advanced threat protection:
- Adaptive baselining with UEBA: Continuously adjust behavior baselines as systems evolve to maintain accuracy in threat detection.
- Decentralize detection: Use edge computing to offload real-time detection closer to endpoints, minimizing response latency.
- Automate low-impact decisions: Use AI to automate low-priority alerts, freeing up human analysts for more complex tasks.
- Data deception traps: Deploy honeypots containing decoy sensitive data to lure attackers and study their techniques.
- Combine EDR with forensic tools: Implement endpoint forensics tools alongside EDR to enhance post-breach investigations.
Advanced Threat Protection Solutions
There are a variety of ATP solutions you can choose from. Below we review three popular ATP products.
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ is an APT solution you can use to automate detection and response in your systems. It is made of three components:
Monitoring and Control
Monitoring and Control features are designed to help you automate visibility tasks and reduce your attack surface. Features include file integrity monitoring, system and application vulnerability detection, report export capabilities, and activity log analysis.
Prevention and Detection
Prevention and Detection features are designed to help you apply next-generation tooling to system protections. It enables you to analyze user, endpoint, and network events and correlate data for greater visibility. Tooling that is incorporated includes next-gen antivirus, endpoint detection and response (EDR), deception technologies, user behavior analytics, and network analytics.
Response Orchestration
Response Orchestration features are designed to help you automate response actions via playbooks. It can help you handle a variety of events, including malware, malicious network traffic, compromised credentials, and infected hosts.
You can incorporate Response Orchestration capabilities into existing protections, such as Active Directory or firewalls. Or, you can use capabilities to respond directly on endpoints.
Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection
Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection is a platform designed to protect Windows 10 users from modern attacks. It combines on-device utilities with utilities and tools in the cloud to provide system-wide protection.
Incorporated utilities and tools include:
- Endpoint behavioral sensors—sensors are embedded in Windows 10 devices and can collect and process event data. Collected data is then sent to a cloud instance of Microsoft Defender ATP for analysis.
- Cloud security analytics—uses big data analytics, machine learning, and proprietary methods to evaluate system data. After analytics are performed, users are provided system insights, alerts to possible suspicious behavior, and recommendations for action.
- Threat intelligence—intelligence is produced by Microsoft hunters and security experts. This intelligence is incorporated into Microsoft Defender ATP to help identify attack methods, processes, and tooling.
Mimecast Advanced Threat Protection
Mimecast Advanced Threat Protection is part of a larger Cyber Resilience Platform offered by Mimecast. It primarily focuses on managing and protecting email security to prevent phishing, malware, and other cyber threats that exploit mail systems.
Mimecast Advanced Threat Protection includes features for:
- Secure email gateways with multi-layered detection
- Targeted threat protection against malware attachments and false links
- Scanning and quarantine capabilities to prevent data leakage
- Secure messaging with built-in encryption
- Sending large files without needing to use filesharing services
Advanced Threat Detection and Protection with Cynet 360 AutoXDR™
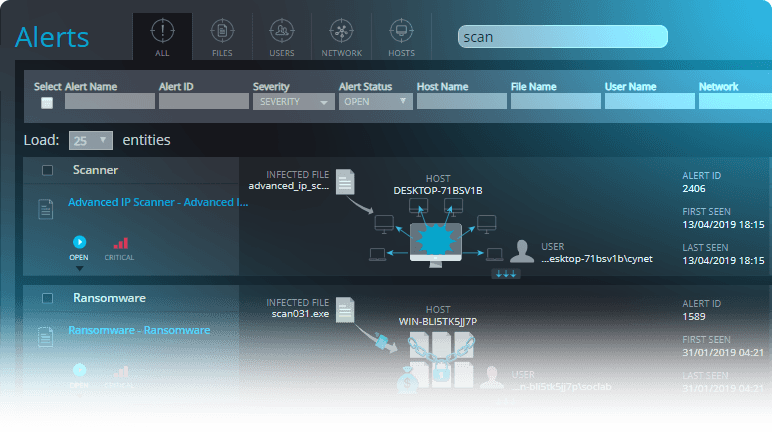
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ is a holistic security platform that provides advanced threat detection and prevention. The platform employs cutting-edge technologies to ensure advanced threats do not slip past your security perimeter. To achieve this goal, Cynet 360 AuotXDR™ correlates data from endpoints, network analytics and behavioral analytics, and presents findings with near-zero false positives.
Block exploit-like behavior
Cynet monitors endpoints memory to identify behavioral patterns that are readily exploited, such as unusual process handle requests. These behavioral patterns lead to the vast majority of exploits, whether new or known. Cynet is able to provide effective protection against Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attacks and more, by identifying such patterns.
Block exploit-derived malware
Cynet employs multi-layered malware protection, including sandboxing, process behavior monitoring, and ML-based static analysis. Cynet also offers fuzzy hashing and threat intelligence. This makes sure that even if an advanced threat establishes a connection with the attacker, and downloads additional malware, Cynet will stop this malware from running, thus preventing any harm from occurring.
UBA
Cynet continuously monitors user behavior, generates a real-time behavioral baseline, and provides alerts when behavior deviation is identified. This deviation in behavior may indicate a compromised user account. Additionally, Cynet provides the ability to define user activity policies, triggering an alert in case of violation.
Deception
Cynet supports the use of decoy tokens—data files, passwords, network shares, RDP, and others—planted on assets within the protected environment. APT actors are highly skilled and therefore might evade detection. Cynet’s decoys lure such attackers, prompting them to reach out and reveal their presence.
Uncover hidden threats
Cynet uses an adversary-centric methodology to pinpoint threats throughout the attack chain. Cynet thinks like an adversary, identifying indicators and behaviors across endpoints, users, files, and networks. They supply a holistic account of the attack process, regardless of where the attack may try to penetrate.
Accurate and precise
Cynet utilizes a powerful correlation engine and provides its attack findings free from excessive noise and with near-zero false positives. This makes the response for security teams easier so they can attend to pressing incidents.
Choose from manual or automatic remediation. This way, your security teams can have a highly effective yet straight-forward way to disrupt, detect, and respond to advanced threats before they have the chance to do damage.
Learn more about the Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ security platform.
See Additional Guides on Key Machine Learning Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of machine learning.
Auto Image Crop
Authored by Cloudinary
- Auto Image Crop: Use Cases, Features, and Best Practices
- 5 Ways to Crop Images in HTML/CSS
- Cropping Images in Python With Pillow and OpenCV
AI Security
Authored by Perception Point
- AI Security: Risks, Frameworks, and Best Practices
- Generative AI in Cybersecurity: 3 Positive Uses and 6 GenAI Attacks
- Top 6 AI Security Risks and How to Defend Your Organization
AI Infrastructure
Authored by Cloudian
Related Posts
Looking for a powerful, cost effective XDR solution?
- Full-Featured XDR, EDR, and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response