Achieved 100% protection in 2024
Stop advanced cyber
threats with one solution
Cynet’s All-In-One Security Platform
- Full-Featured EDR and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response
Written by: Ronen Ahdut
Cynet CyOps is carrying out ongoing threat intelligence gathering and analysis efforts to protect Cynet customers. Considering the recent conflict between Russia and Ukraine which have active cyber warfare aspects, we would like to ensure you that we are constantly monitoring the developments, events, publications, and other sources of data to make sure Cynet360 can detect and prevent malware variants deployed as part of the cybernetic warfare.
Cynet is detecting and preventing the following variants affiliated with the recent conflict:
In this report you can find examples of malware variants (Wipers in this case) deployed by Russia during the conflict, and the detections triggered by Cynet360 upon its execution.
A new form of disk-wipe malware dubbed as “HermeticWiper” was revealed, which is a destructive malware that has been observed recently in Ukraine.
The malware is a disk wiper that targets the MBR for corruption – – thus blocking the user from accessing the host.
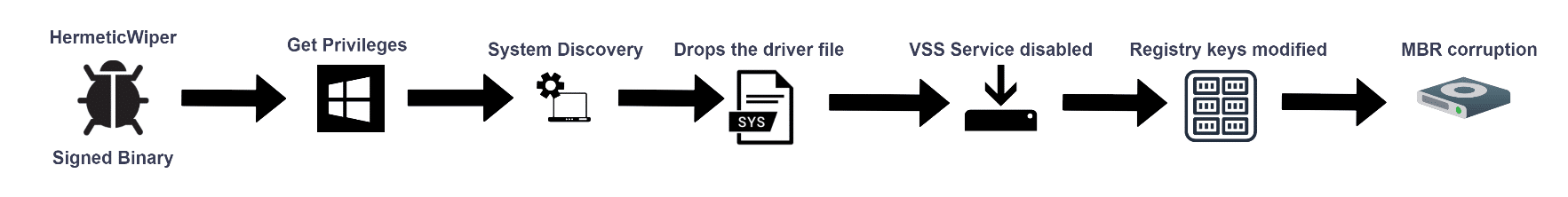
In this section, we will visit the HermeticWiper threat. We will introduce its new capabilities and execution flow.
In late February the tension between Russia and Ukraine has escalated which led to ongoing cyberattacks and the birth of HermeticWiper which was built to destroy Ukraine organizations’ systems by corrupting the physical disks,.The authors use a 32-bit executable which is digitally signed with a valid signature from a company called “Hermetica Digital Ltd”.
The source of the malware name is taken from the digital signature by Hermetica combined with the purpose of the malware.
During the execution, this wiper also disables the volume shadow copy services to make sure that the recovery process is not an option and disables the ability to generate a memory crash dump using the registry keys on Windows machines to gain the final goal of MBR corruption.
In this section, we will analyze a random sample of HermeticWiper malware.
Samples of HermeticWiper are being uploaded daily to MalwareBazaar(by abuse.ch):
HermeticWiper is a 32-bit portable executable:
HermeticWiper uses a certificate which is digitally signed by “Hermetica Digital Ltd”
HemeticWiper uses three functions for “Get Privileges”:
Part of the strings that HermeticWiper leverage on the dynamic execution:
The following driver file is installed as a service and drops at “C:WindowsSystem32drivers[drivername].sys
The driver is responsible for deleting the service that was created previously.
HermeticWiper leverages legitimate software in order to use the driver capabilities for various disk functionality (such as resize partitions, delete, etc.) and drops the driver at system32 that will be executed as a service and eventually be deleted.
Just before the MBR corruption process, HermeticWiper disables the crash dump generation using the registry key → “SYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlCrashControl”

Upon dynamic execution, the registry key value for “CrashDumpEnabled” has changed to 0x0.
The final phase of the HermeticWiper is a disk corruption:
The CyOps team is working around the clock to enhance detections by implementing IOCs, memory patterns SSDEEP, etc.
As you can see below we took a random HermeticWiper sample and executed it in our lab..
Note that our environment action is set to alert only so as not to interrupt the ransomware flow.
This lets Cynet detect every step of the attack.
File Dumped on the Disk – Cynet’s AV/AI engine detects a malicious file that was dumped on the disk.
Attempt to Run – Cynet’s AV/AI engine detects a malicious file that was loaded into memory:
Malicious Binary – Cynet detects a file that is flagged as malicious in Cynet’s EPS (endpoint scanner) built-in threat intelligence database. This database contains only critical IOCs (such as IOCs of ransomware, hacking tools, etc.):
Malicious Binary – Process Create Malicious File – This alert triggers when Cynet detects a process that creates a file which is either flagged as malicious in Cynet’s Threat Intelligence database or associated with suspicious patterns (such as loaded to sensitive directories).
Threat Intelligence Detection – Malicious Binary – Blacklist – This alert triggers when Cynet detects a file that is flagged as malicious in Cynet’s internal threat intelligence database:
Malicious Binary – Cynet detects a file that is flagged as malicious in Cynet’s EPS (endpoint scanner) built-in threat intelligence database. This database contains only critical IOCs (such as IOCs of ransomware, hacking tools, etc.):
WhisperGate is a destructive malware that has been observed recently in Ukraine. It masquerades as Ransomware by demanding a ransom in exchange for restoring the systems. However, it actually wipes the MBR of the machine and alters files – thus destroying the hard drive completely.
First seen in the wild on Jan 13th by Microsoft MSTIC, WhisperGate operators have been dubbed as DEV-0586. A WhisperGate attack is composed of several stages. While it behaves as Ransomware and demands funds from the victim to access the files, it cannot revert the encryption. In fact, no such option is available inside the malware.
The ransom “note” only exists to mask the destructive characteristics of the Wiper malware which is a class of malware whose intention is to wipe the hard drive of the computer it infects, probably due to tension between Russia and Ukraine, and minimize accusing fingers.
WhisperGate uses a legitimate service (Discord) to spread an additional payload. This is used to bypass any firewall block or to not seem suspicious to SOC operators inspecting the activity at the time.
While no further activity has been seen since the first wave, we estimate that, due to the tension between Russia and Ukraine, we might see similar activities in the near future.
How initial access is achieved is still unknown. WhisperGate is estimated to be using a supply chain attack.
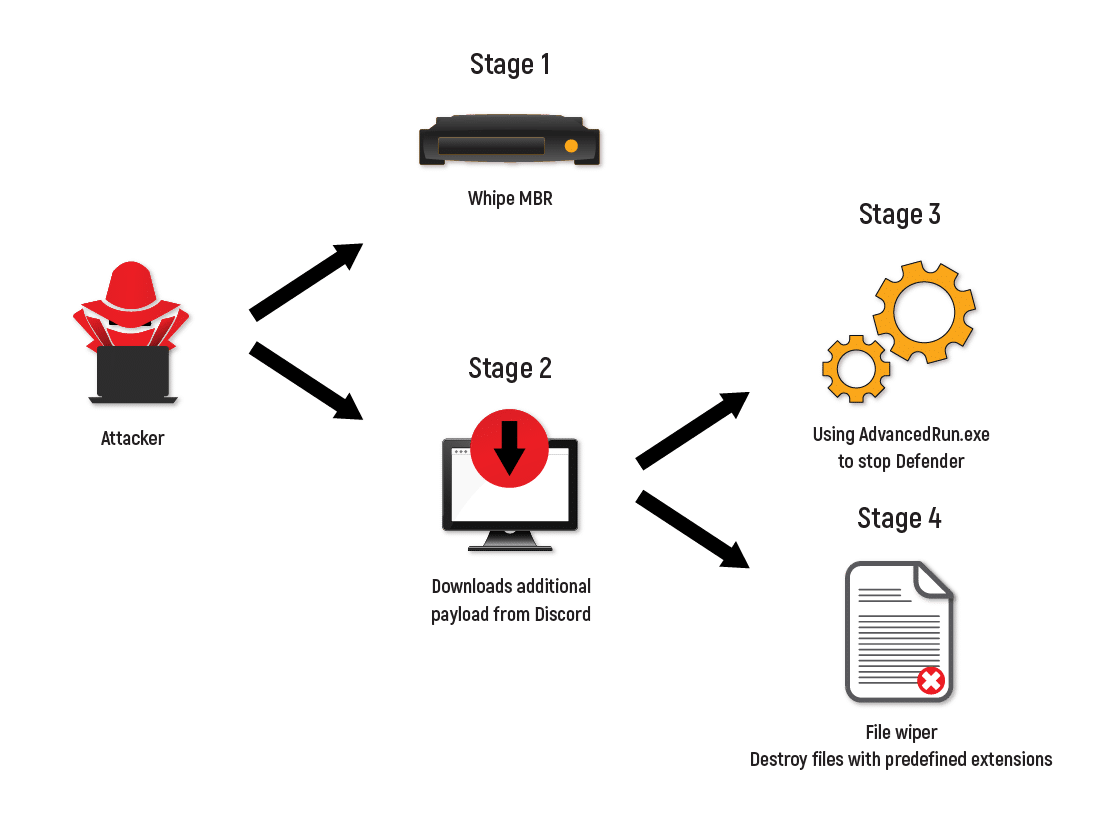
Stage 1: Wiping the MBR
First, the attacker wipes the MBR. Then, when restarting the system, the compromised host is presented with the following message:
A few worthy mentions:
WhisperGate uses the same Bitcoin wallet for all victims.
All victims receive the same ransom amount.
Only TOX (a secure chat service) is available for contact.
Most Ransomware operators offer a free example of decryption unlike WhisperGate.
This strengthens the hypothesis that WhisperGate is only masquerading as Ransomware.
Stage 2: Downloading Payload
This stage is for loading. By using a predefined URL (Discord has been seen in this vector) WhisperGate will download and load a VBS script as well as additional payloads: AdvancedRun by nirsoft to elevate privileges and a second Wiper for specific file types hardcoded in the malware.
Stage 3: Script Execution
In this stage, the attacker will execute the script while excluding the entire C: drive from Windows Defender’s detection tactic called impair defenses by using a PowerShell command. The payload is able to stop windows defender, and even delete the windows defender AV folder from the system.
Stage 4: File Wiping
In the fourth stage, the attacker will initiate the Wiper. It is predefined to overwrite files for destruction and add a random extension.
The predefined file extension that the malware will overwrite:
Blockchain Analysis:
The Bitcoin address associated with the malware had no transactions apart from one of approximately five dollars.
The transaction is dated: January the 14th, 2022.
The MBR Payload stub as seen in the analysis of Stage 1:
The payload download from Discord from stage 2:
Similarity to other Ransomware found in the Darknet:
We have detected a Ransomware that seems similar to the activity seen by WhisperGate.
H3llB0rn Ransomware ransom note:
Note the similar usage of a Bitcoin address and the missing contact methods, which are uncommon in Ransomware activity today.
In addition to detecting all stages that dropped on the disk, Cynet also detects the malicious binary of the files:
Since WhisperGate alters the MBR by writing its stub to the following –
Cynet’s RAW Disk Write alert will be triggered via a specific mechanism dedicated to MBR altering protection.
IsaacWiper is the third wiper malware that has been identified targeting Ukrainian organizations.
It acts similar to both previously seen wipers and will corrupt the system MBR.
IsaacWiper will also fill all disks on the system with random content until no available space remains.
It is the latest wiper that has been seen in the ongoing cyber warfare between Russia and Ukraine.
IsaacWiper is the “simplest” form of the trio.
While WhisperGate used Discord as a sophisticated C2, and Hermetic used a worm and a ransom as separate parts, IsaacWiper remains simple by “just” wiping the MBR and filling the hard drives with random data until full.
While the initial vector is still uncertain, IsaacWiper was found on an endpoint that had seen the usage of RemCom: “RemCom is a small (10KB UPX packed) remote shell/telnet replacement that lets you execute processes on remote windows systems, copy files on remote systems, process their output, and stream it back.”
In addition to detecting all stages that dropped on the disk, Cynet also detects the malicious binary of the files:
Wipers are destructive tools with one sole purpose; to inflict damage and destroy their target without a recovery option.
These attacks that have emerged during the conflict between Russia and Ukraine through an unknown threat actor are believed to be nation-state threat-related.
We believe that further observations related to the activity of this Malware will come soon, especially as tension keeps building up during the war..
As demonstrated above, Cynet detection and prevention mechanisms are actively detecting and mitigating the plethora of wipers introduced during this conflict.
On top of that, Cynet Research group is working around the clock to deploy new rules and policies to stay ahead of these attacks.
Search results for: