In this article
Microsoft MSHTML Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
As part of our ongoing threat intelligence efforts to discover emerging threats and vulnerabilities, the CyOps team would like to bring a new risk to your attention.
On September 7th, 2021, Microsoft disclosed a new zero-day vulnerability carrying the identifier CVE-2021-40444 which is already being exploited in the wild. In this update, we will cover how the vulnerability works and how you can defend against it.
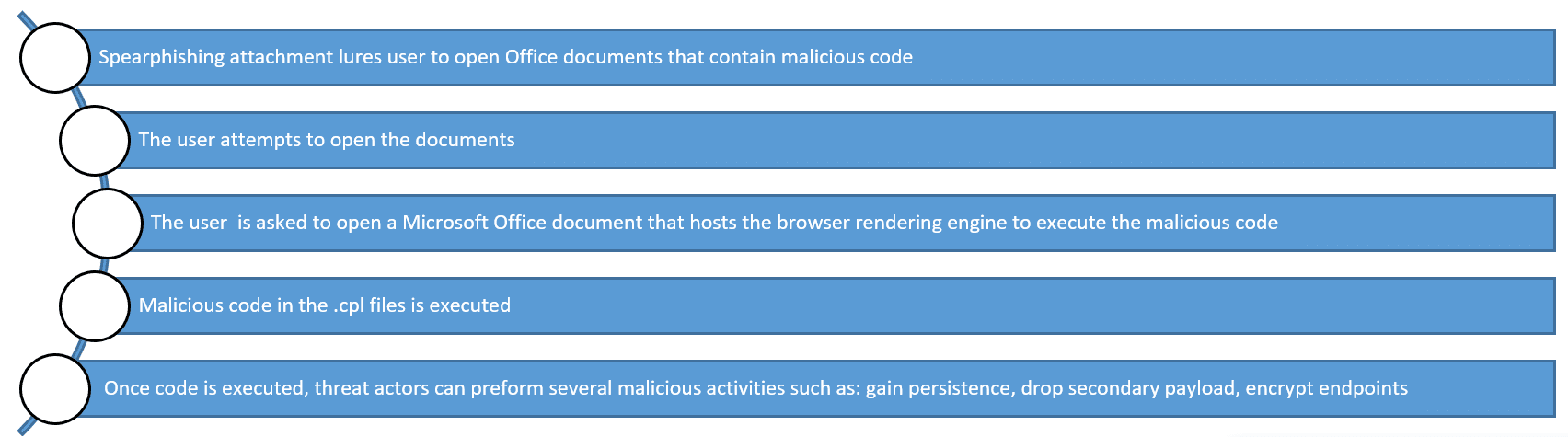
CVE-2021-40444 is a remote code execution vulnerability that allows an attacker to run arbitrary code on a victim’s machine via ActiveX control usually sent to the victim via spear-phishing. Based on CVE-2021-40444, an attacker can craft a malicious ActiveX control to be used by a Microsoft Office document that hosts the browser rendering engine. The attacker would then have to convince the user to open the malicious document. Once the user opens the document, the vulnerability is then exploited and the attacker can execute arbitrary code.
The new zero-day is a critical risk vulnerability in the Trident MSHTML rendering engine. Threat actors exploiting this vulnerability are targeting and attacking Office 365 on numerous OS versions and Office 2019 on Windows 10.
This exploit uses ActiveX controls and .cpl files and is a highly sophisticated attack.
ActiveX controls are small program parts that can be used to create and execute applications that work over the Internet through web browsers such as online Office apps.
On top of that, ActiveX allows applications to share functionality and data through web browsers.
This ActiveX vulnerability and many more can be deployed through malicious Microsoft Office documents and are often used in spear-phishing campaigns.
In this case, the malicious code is hidden in .cpl files which are used for control panel items, but are actually similar to DLL files and can be executed.
In order for this attack to succeed the differential between the user’s privilege is critical as executing these malicious documents with administrators poses additional risks.
Mitigations techniques
Each one of these will protect your machines from the attack:
Do not open office documents from people you don’t know!
1)Microsoft’s Protected View is a protection method that is enabled by default when opening Office documents from the internet or from unsafe locations. These documents will be opened in read-only mode to prevent execution of malicious content. You should not disable this protection and not click on buttons asking you to turn it off. Additionally, IT admins should make sure all office users are running with this feature enabled.
2) Enabling Application Guard is a security container that isolates unknown documents from the rest of your personal data. This can be enabled from “Windows Turn Off and On” settings page.
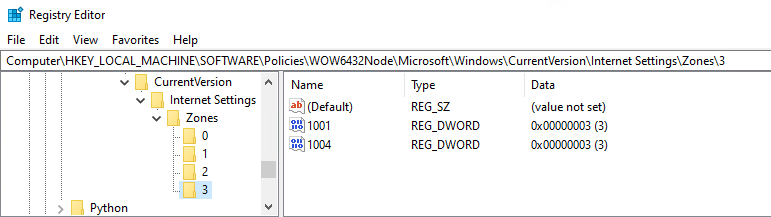
3) Disabling ActiveX control can mitigate this attack, by modifying the relevant registry keys.
To modify the registry keys and disable ActiveX controls please follow the instructions below:
Download here and execute the following file → “disable-activex.reg” after the execution of the file reboot the machine. (This file needs to be executed with elevated privileges).
This file was published by MS and disables ActiveX in your registry.
Another option that doesn’t include downloading the file is to simply create a text file called “disable-activex.reg”
Copy-paste the text box below and change the file extension to .reg
| Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\0] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\1] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\2] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\3] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\0] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\1] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\2] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\3] “1001”=dword:00000003 “1004”=dword:00000003 |
This is the best temporary fix, as there is no patch available by Microsoft at the moment.
The results can be found via the Registry Editor on the following reg keys:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\
In case you wish to undo this step, you can delete the registry keys that were added.
Important note – Cynet can automate a temporary mitigation recommended by Microsoft that can be done using Cynet. Please download or create the file (disable-activex.reg”) on a machine on which you can access the Cynet UI console.
Follow this instructions to complete this task through Cynet UI.
Workflow:
- First, we will create a folder called “Disable ActiveX” that will contain two crucial files.
- Place the disable-activex.reg file you have created or downloaded in this folder.
- Create a batch file called starter.bat and place it over the Disable ActiveX folder.
- starter.bat should contain the following lines:
- @echo off
- cmd.exe /c reg import disable-activex.reg
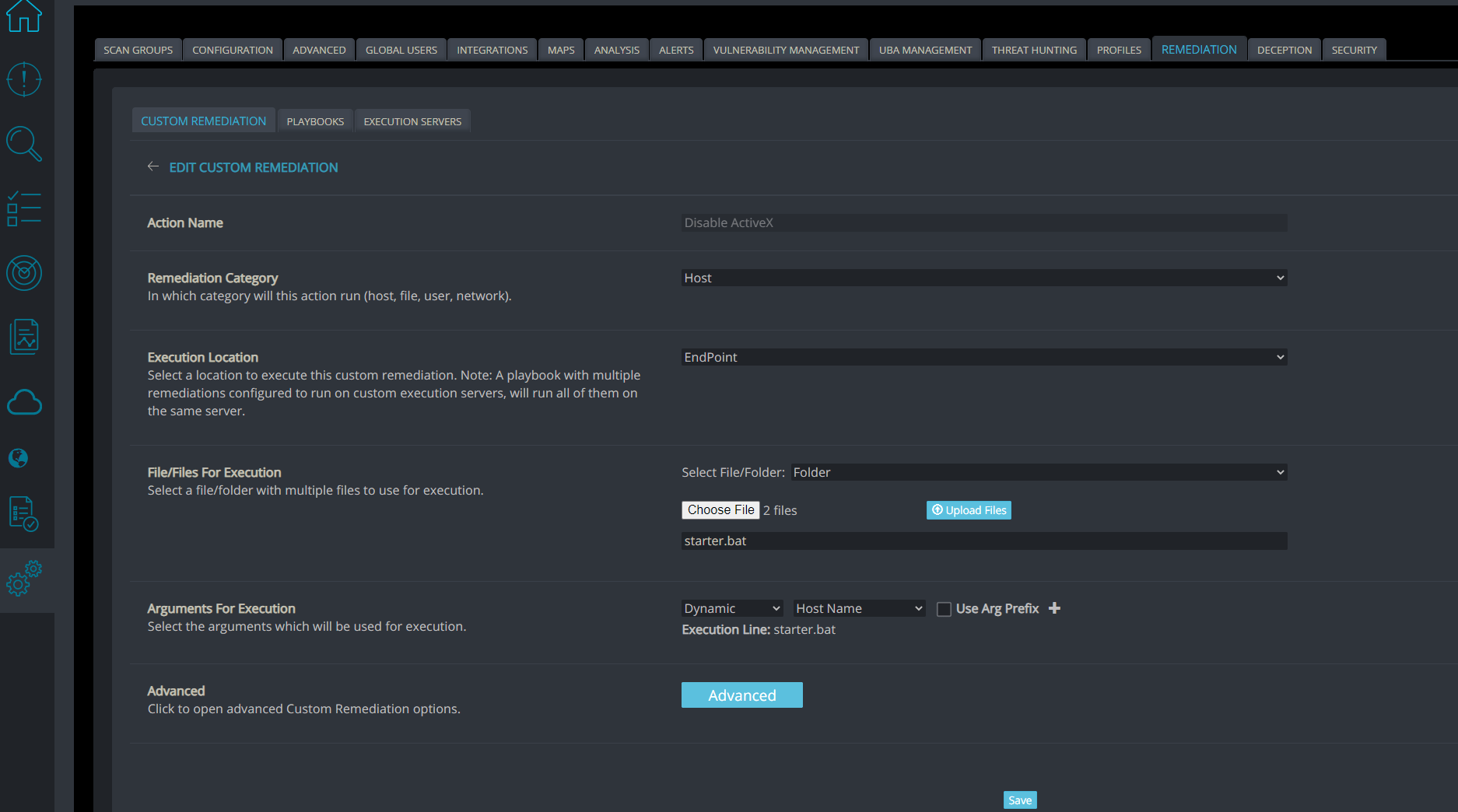
Now we are ready to create a custom remediation that will execute the script on the machine.
Settings→Remediation→Custom Remediation→Create:
- Action Name: Disable ActiveX
- Remediation Category: Host
- Execution Location: Endpoint
- Select File/Folder: Folder
- Click Choose file and choose the folder we have created.
- Upon adding this folder click upload files.
- File to execute: starter.bat
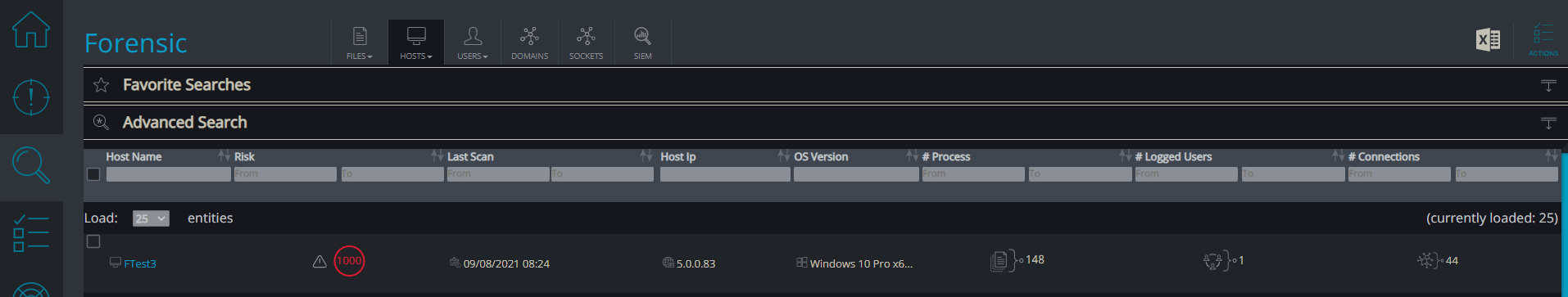
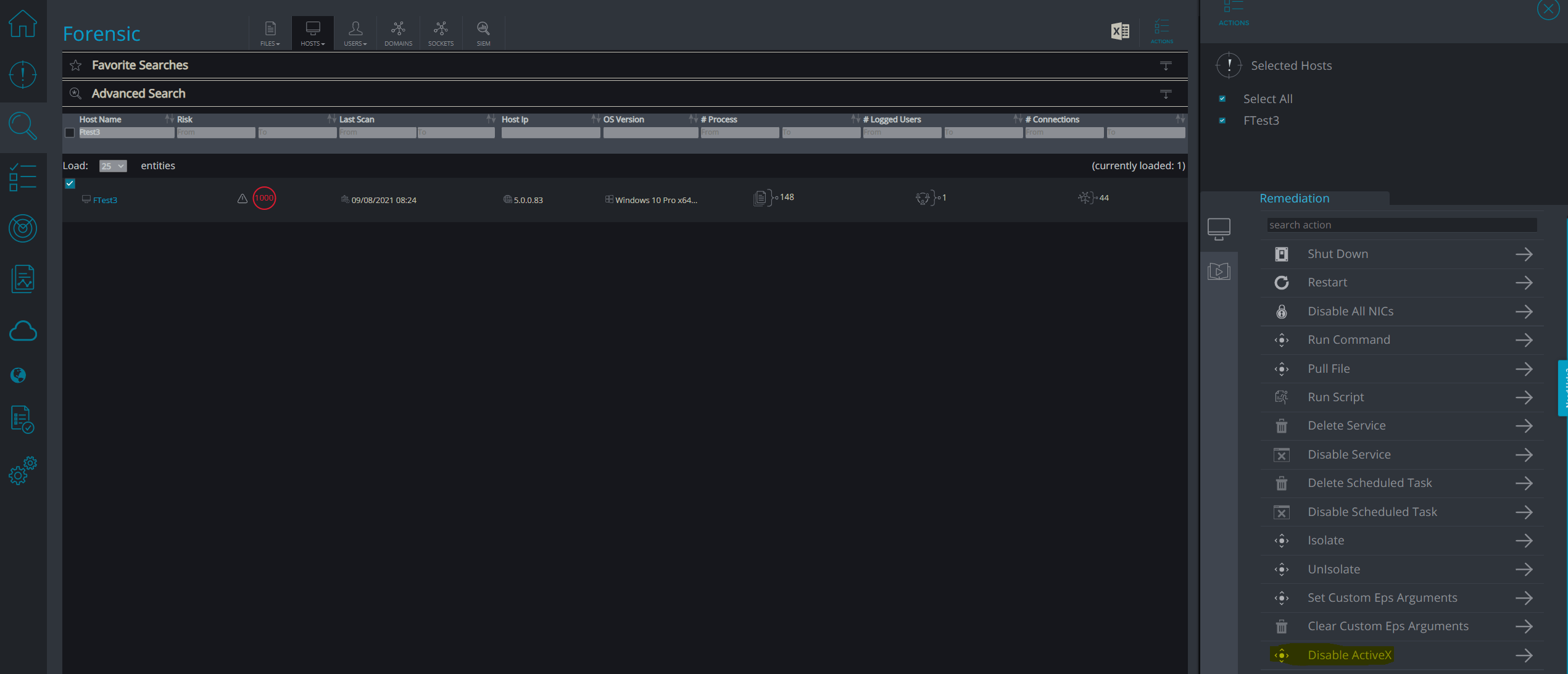
Then go to “Hosts” → “Forensic”, under the “Forensic”tab:
Choose the machines you want to enumerate, and click on Actions.
Then execute the custom remediation we created:
This action will be executed on all hosts you have selected.
As always, we are available for any questions or concerns and in any case further assistance is required.
Indicators Of Compromise
Cynet Threat Intellegnce team observed several IOCs as part of the ongoing hunting efforts that seem to be related to the vulnerability exploitation as they were using ActiveX. Below you can find several IOCs for these attacks:
| SHA-256 | 938545f7bbe40738908a95da8cdeabb2a11ce2ca36b0f6a74deda9378d380a52 | Weaponized document |
| SHA-256 | 199b9e9a7533431731fbb08ff19d437de1de6533f3ebbffc1e13eeffaa4fd455 | Weaponized document |
| SHA-256 | 5b85dbe49b8bc1e65e01414a0508329dc41dc13c92c08a4f14c71e3044b06185 | Weaponized document |
| SHA-256 | d0fd7acc38b3105facd6995344242f28e45f5384c0fdf2ec93ea24bfbc1dc9e6 | Malicious HTML Code |
| SHA-256 | 1fb13a158aff3d258b8f62fe211fabeed03f0763b2acadbccad9e8e39969ea00 | Cab file |
| Domain | hidusi[.]com | C2 Server |
| IP | 23[.]106[.]160[.]25 | C2 Server |
Contact Cynet CyOps
(Cynet Security Operations Center)
The Cynet CyOps available to clients for any issues 24/7, questions or comments related to Cynet 360. For additional information, you may contact us directly at:
CyOps Mailbox – [email protected]
CyOps Team Leader – [email protected]
CyOps Manager – [email protected]
Israel +972 72-3369736
UK +44 2032 909051
US +1 (347) 474-0048
Related Posts
Looking for a powerful, cost effective XDR solution?
- Full-Featured XDR, EDR, and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response