April 2022 Ransomware Activity Report
Written by: Maor Huli
In month April, the ransomware that will be introduced will be:
- Axxes
- Blaze
- BlockZ
- Democracy Whisperers
- Medusa
- Parker
- Snatch
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Orion is an integral department in Cynet’s research team that works around the clock to track threat intelligence resources, analyze payloads, and automate labs to ensure that our customers are protected against the newest ransomware variants. In these monthly reports, Orion reviews the latest trends identified in Bleeping Computer – the most up-to-date website that summarizes the newest ransomware variants – and shares how Cynet detects against these threats.
CYNET 360 AutoXDR™ VS RANSOMWARE
- Observed since: April 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: RSA + AES.
- Ransomware extension: .axxes
- Ransomware note: RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt
- Sample hash: ec7fbdf548bd27bb5076dd9589e1b87f3c5740da00e77c127eb4cd4541d7d6f7
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
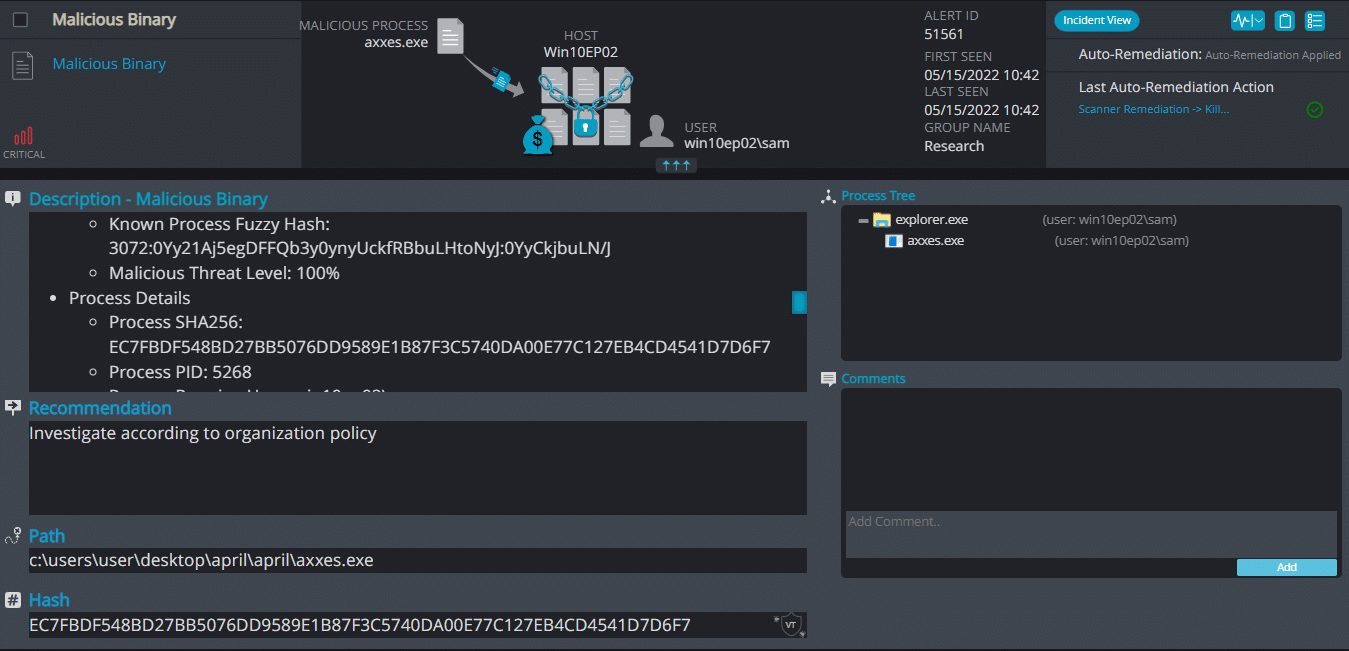
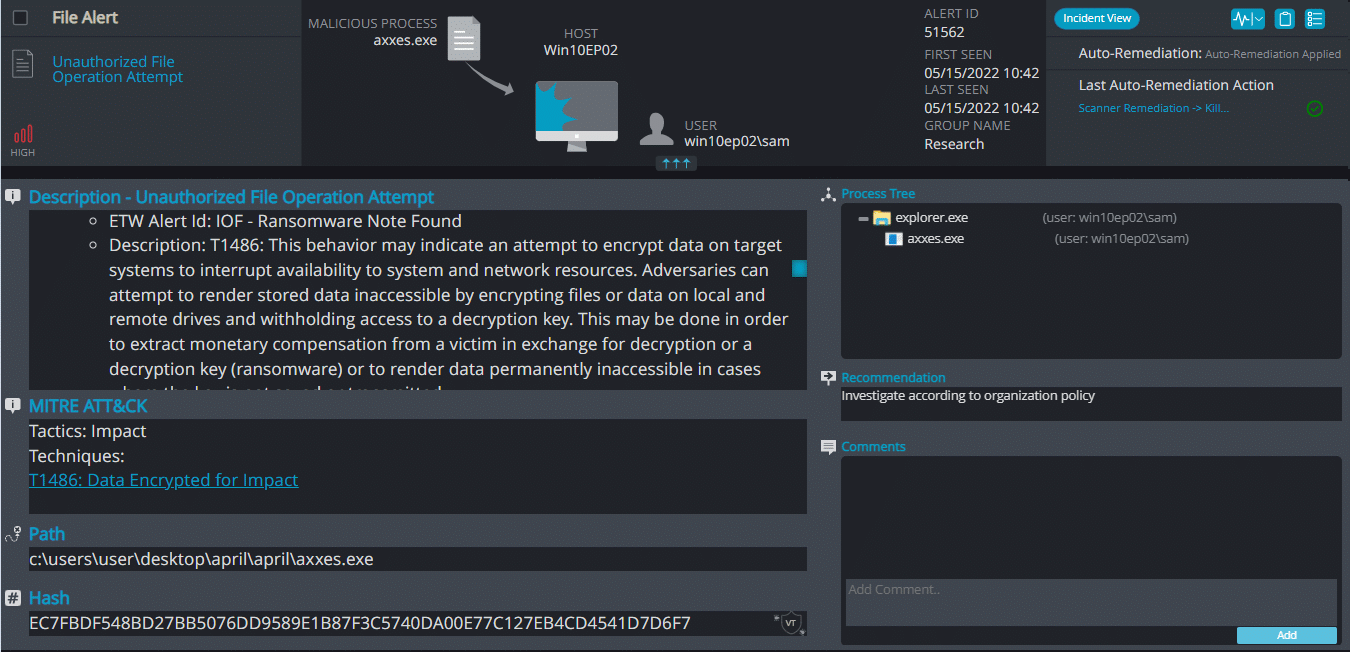
Axxes ransomware renames the encrypted files with .axxes in the extension:
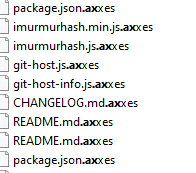
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt:
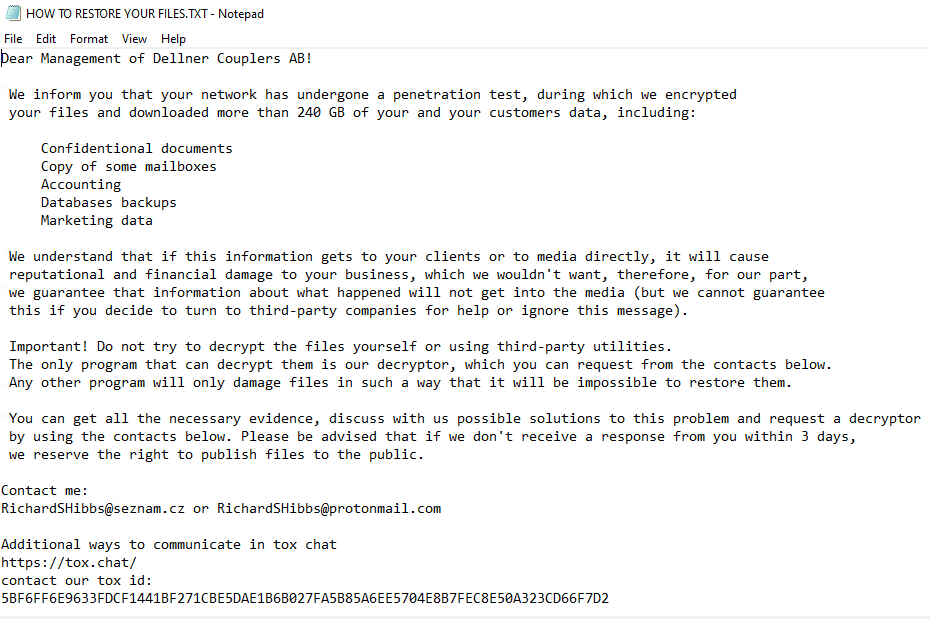
Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains only the encryption key:

Blaze Ransomware
- Observed since: December 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: RSA.
- Ransomware extension: .blaze
- Ransomware note: How To Decrypt.txt
- Sample hash: 25835a890a218fd26bfd8b23696576402b5eb8a4c9af4a51529e14c4f00a9cce
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
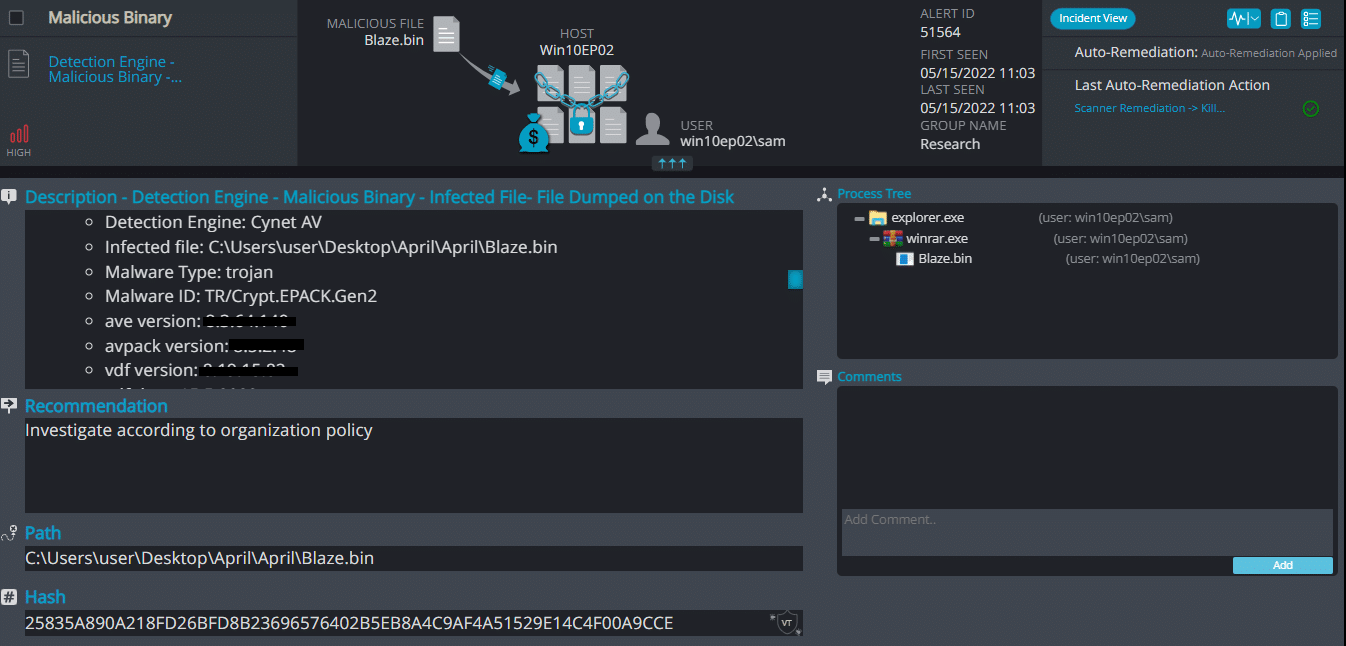
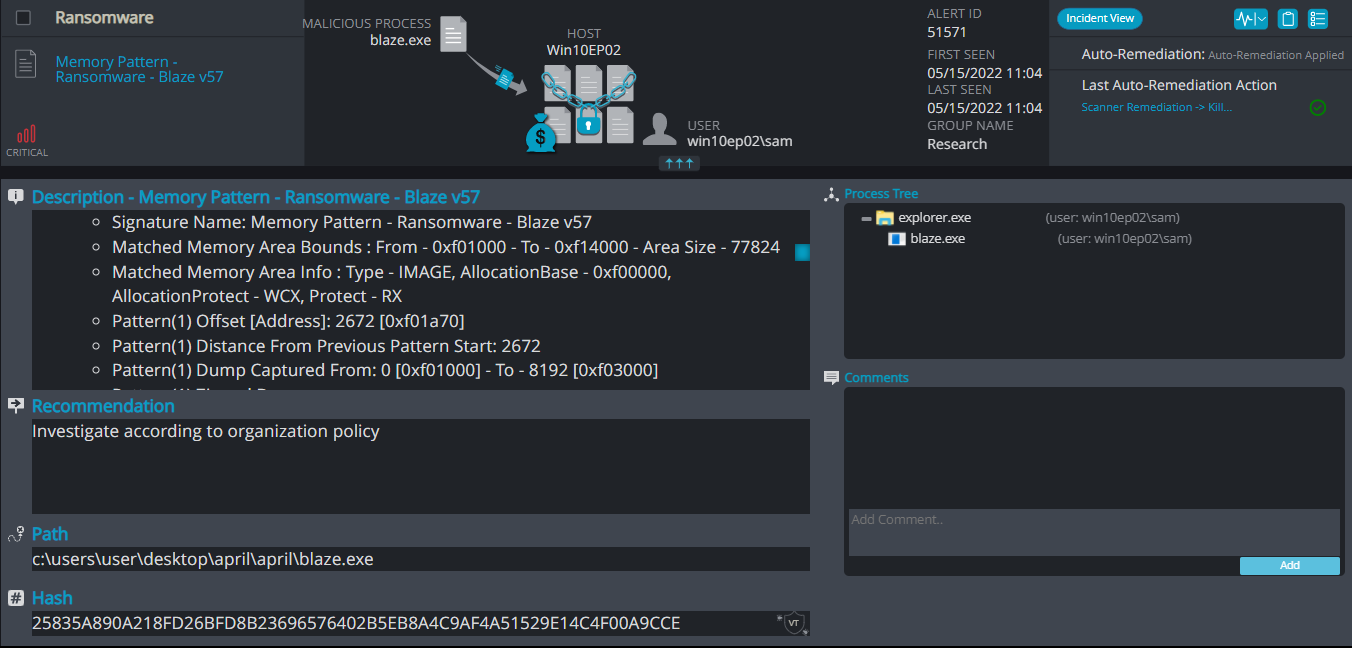
Blaze ransomware renames the encrypted files with .blaze in the extension:

Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as How To Decrypt.txt:

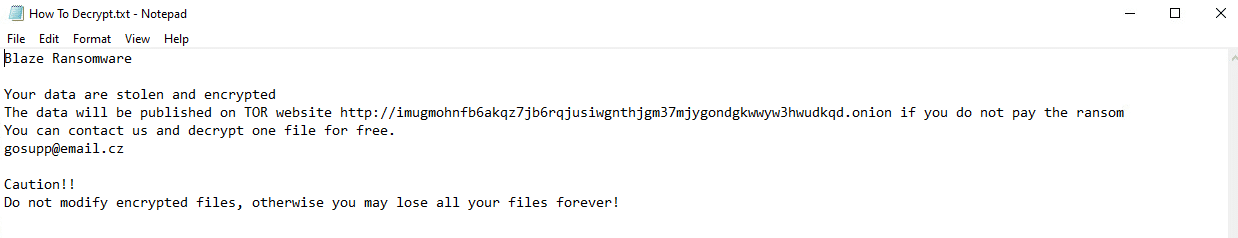
Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains general information and the attacker’s contact information:
BlockZ Ransomware
- Observed since: April 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA.
- Ransomware extension: .blockZ
- Ransomware note: How To Restore Your Files.txt
- Sample hash: 856d9e698f240a21db57f404fea33ee65cd0458f31a9d0fca7044962204484c9
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
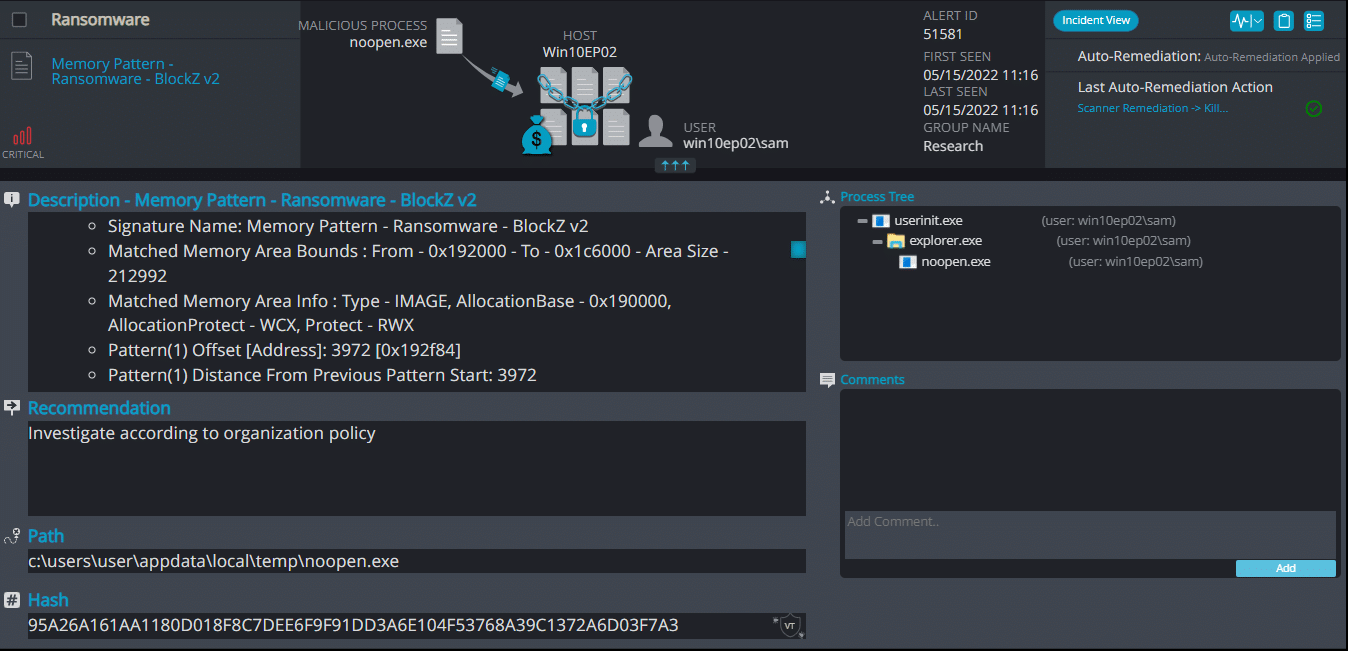
BlockZ ransomware renames the encrypted files with .blockZ in the extension:

Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as How To Restore Your Files.txt:

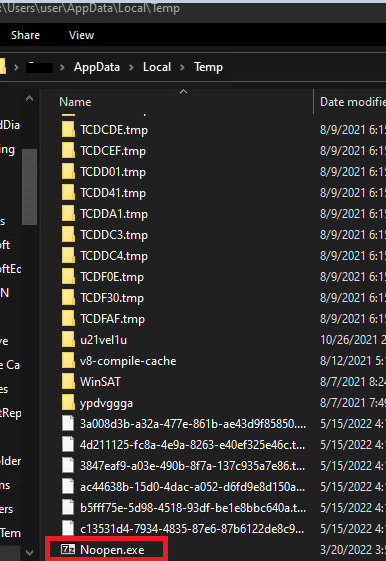
Upon execution, it first drop a file in the path “c:\users\*user\appdata\local\temp\” with the name of Noopen.exe:
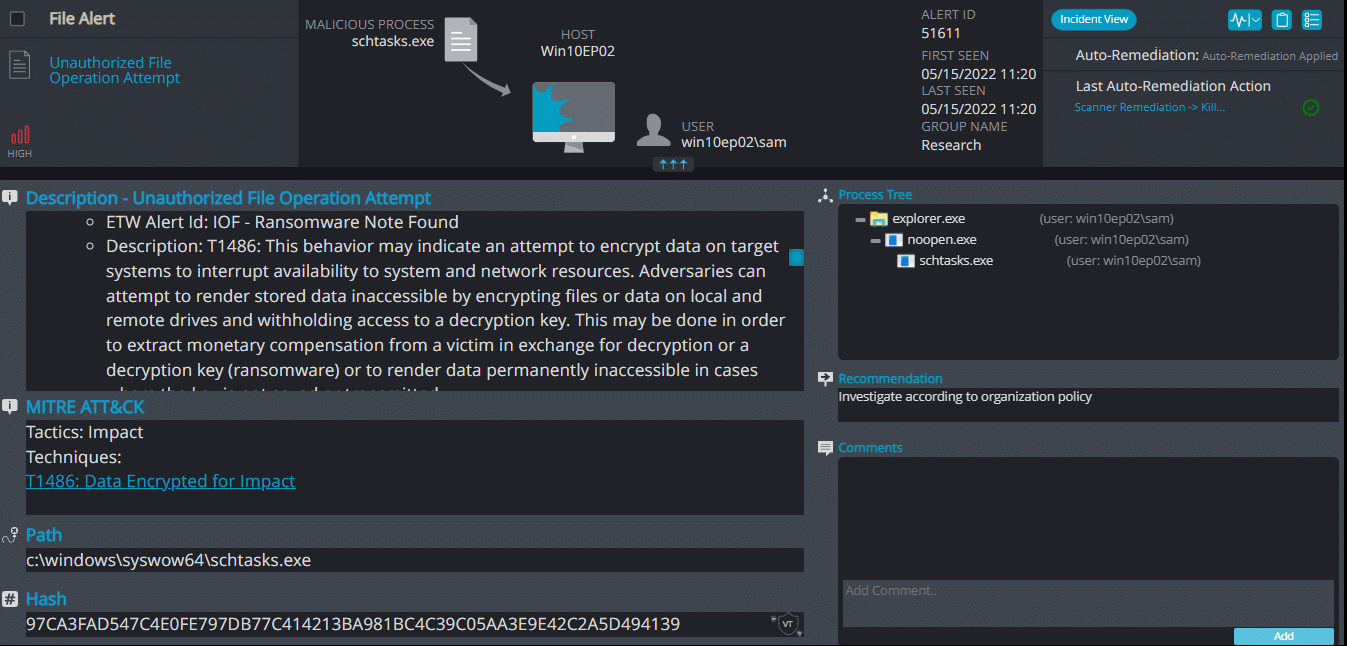
Once executed the dropped file it changes the process name to schtasks.exe and it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains contact information, warnings, and decryption test for 1 file:
DemocracyWhisperers Ransomware
- Observed since: April 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .democ
- Ransomware note: Restore Files.txt
- Sample hash: 59e0e38b068f736e7f618c714a116ad13fb50a1932942cff9e474de317fb4592
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
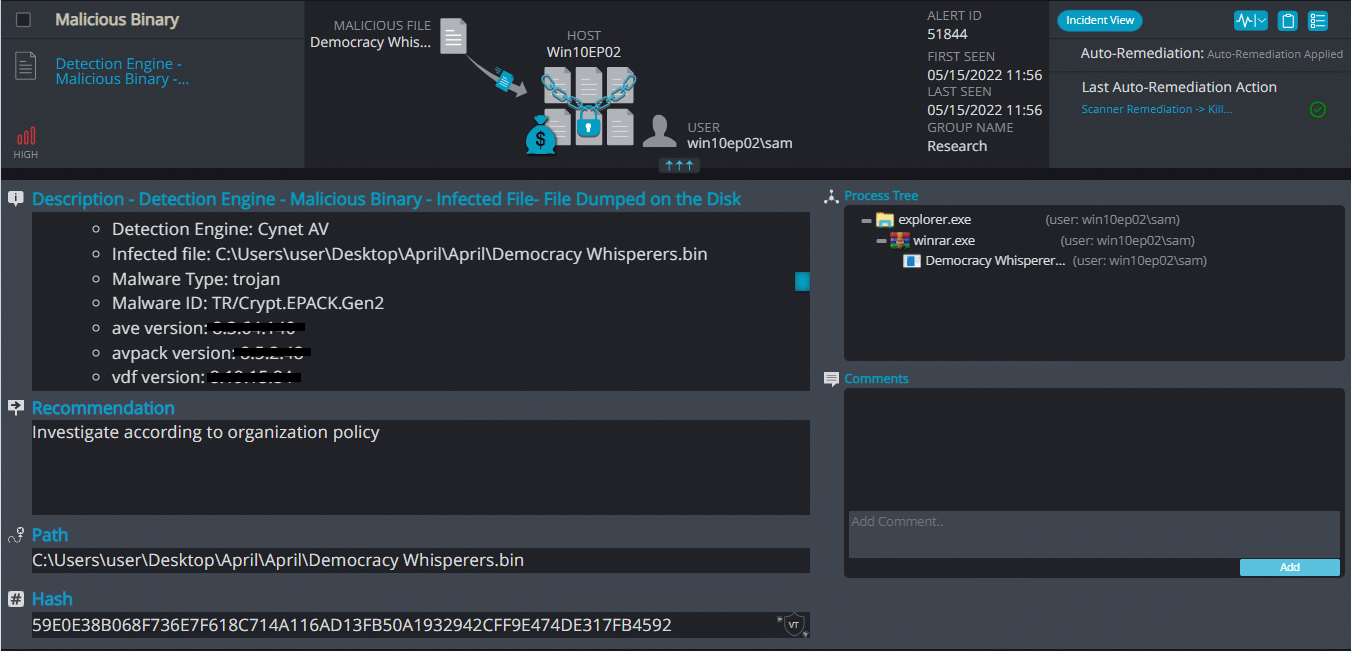
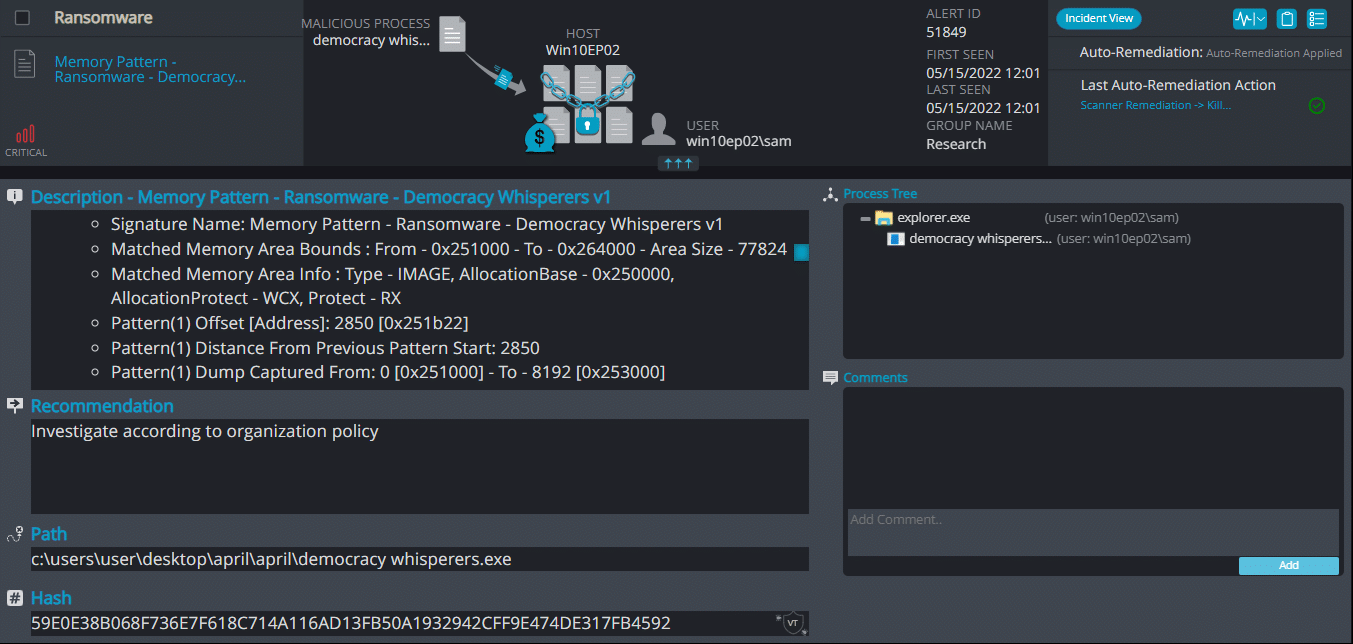
DemocracyWhisperers ransomware renames the encrypted files with .democ in the extension:
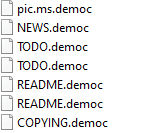
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as Restore Files.txt:
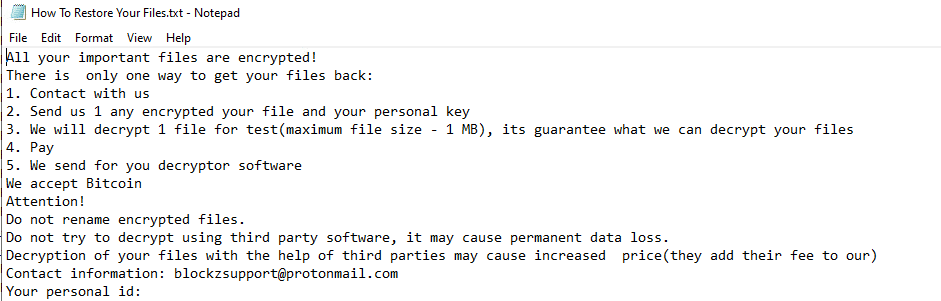
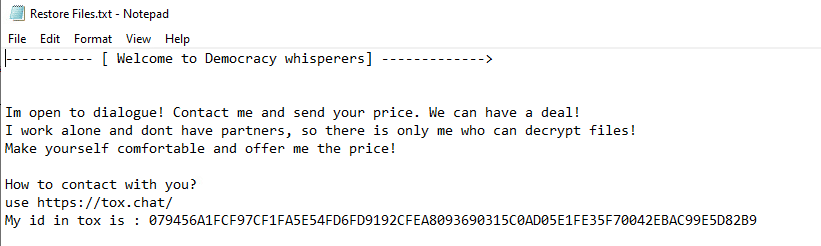
Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains instructions and the attacker’s contact info:
Medusa Ransomware
- Observed since: Late 2019
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .stopfiles
- Ransomware note: Recovery_instructions.html
- Sample hash: 2ca49be7f3eac14dfbf086ad11ce1235079b4fa96b7d8634a53403cfcf592969
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
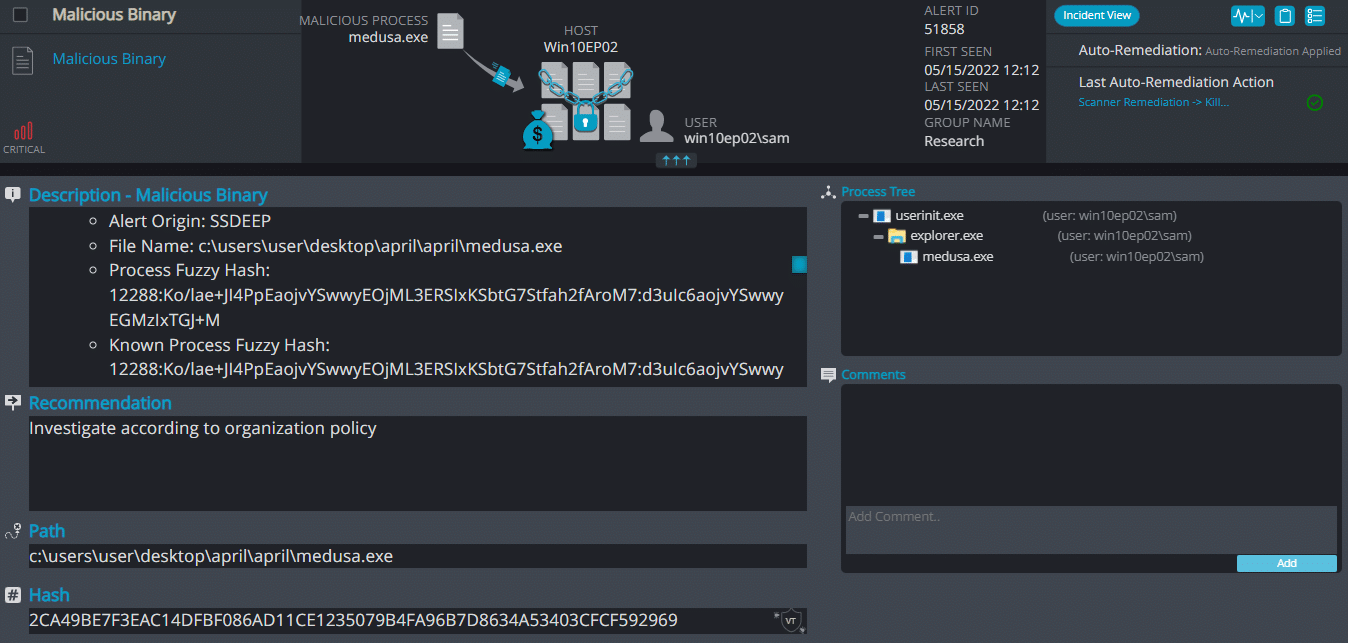
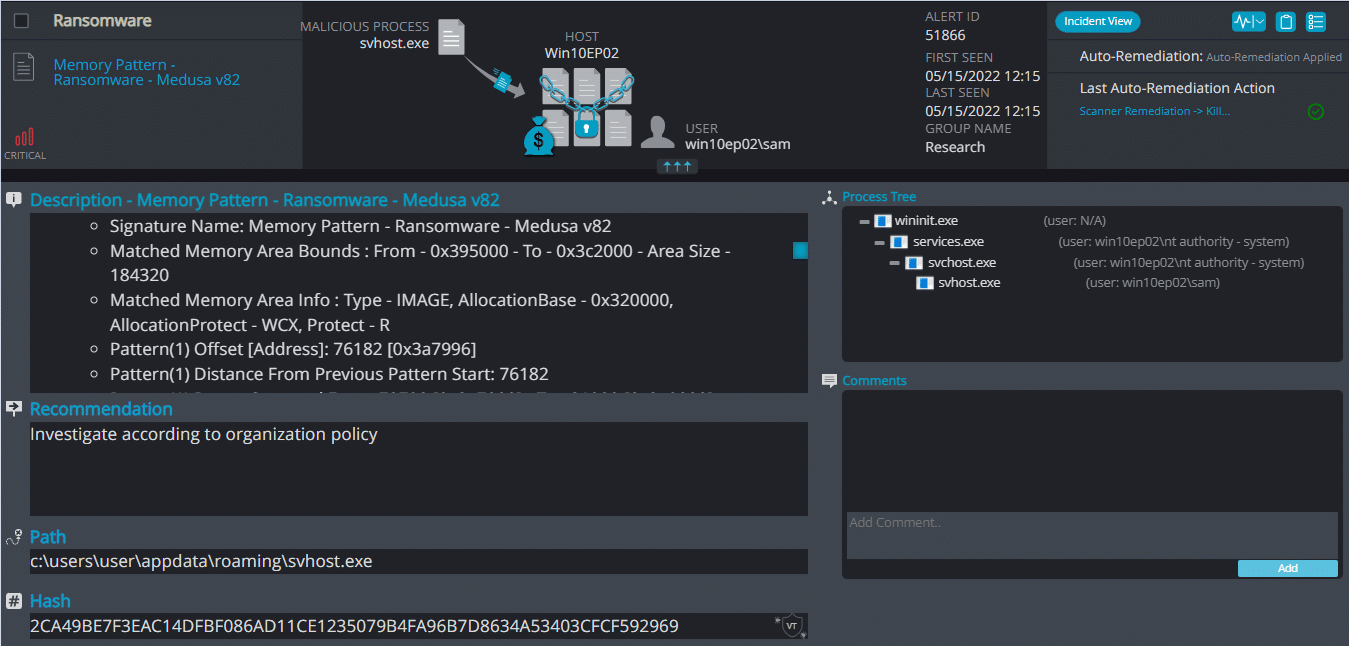
Medusa Overview
Medusa ransomware renames the encrypted files with .stopfiles in the extension:
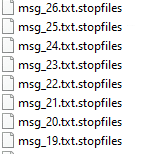
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as Recovery_instructions.html:

Upon execution, it inject itself to svchost and it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains instructions and the attacker’s contact info:
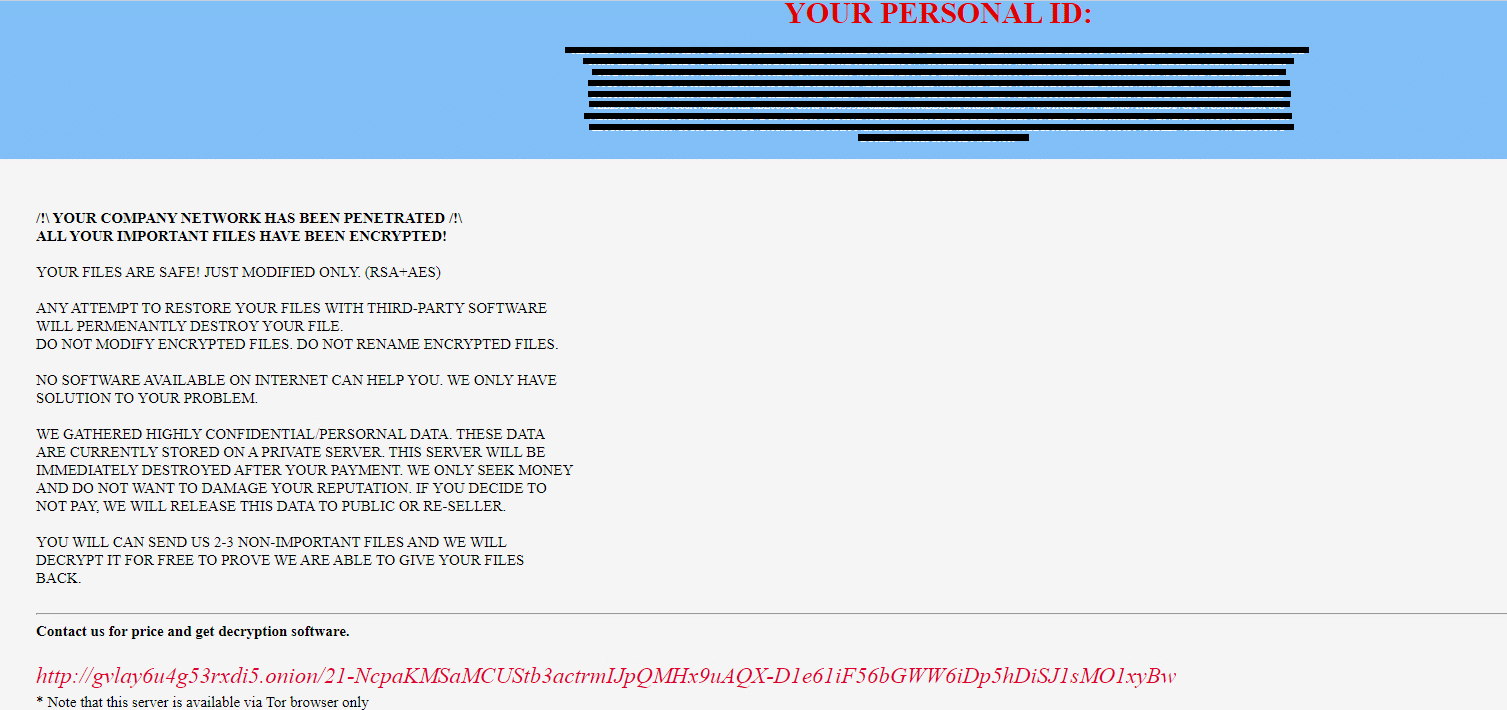
Parker Ransomware
- Observed since: April 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .PARKER
- Ransomware note: RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt
- Sample hash: 39a044db72d3ca39122af249cd60660d7e200366af958c762910605eaed020cb
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
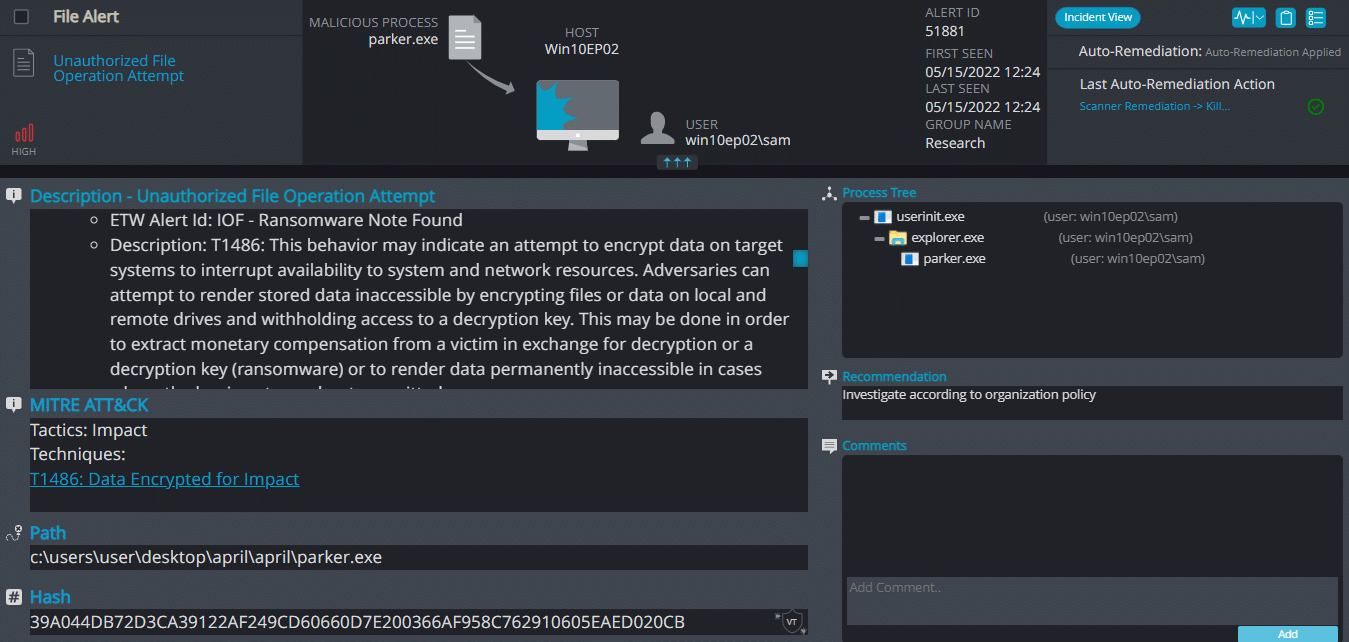
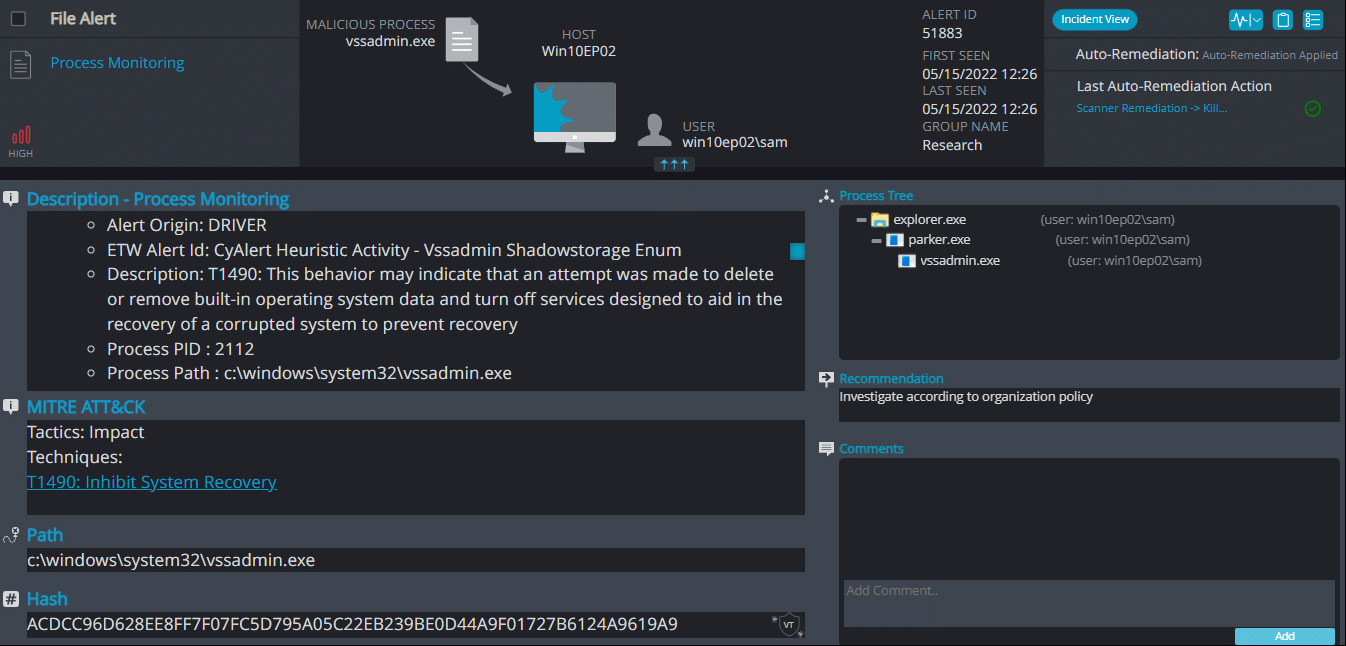
Parker Overview
Parker ransomware renames the encrypted files with .PARKER in the extension:
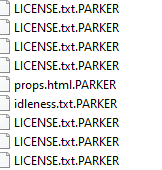
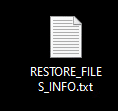
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt:
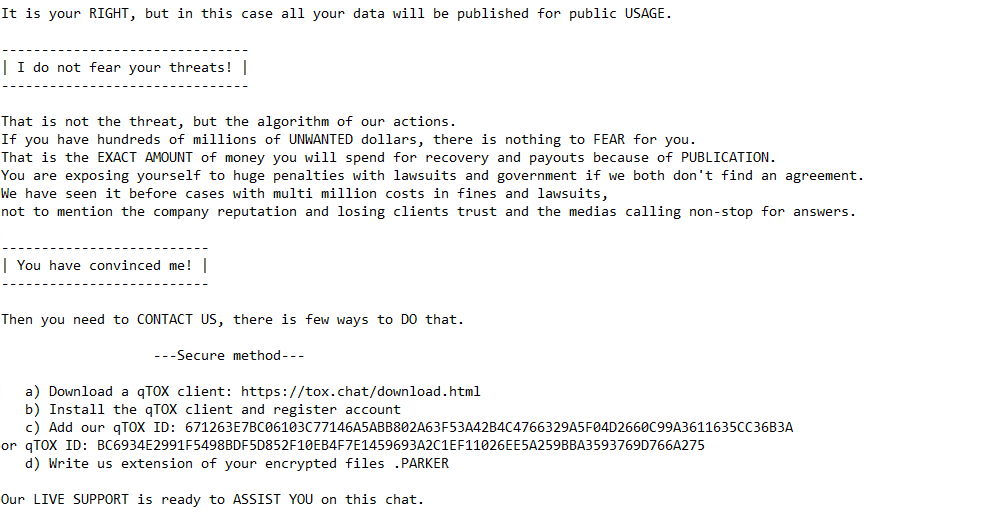
Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains instructions, threats for data publication, and the attacker’s contact info: 

Snatch Ransomware
- Observed since: December 2018
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .sdhvqq
- Ransomware note: HOW TO RESTORE YOUR FILES.TXT
- Sample hash: 25835a890a218fd26bfd8b23696576402b5eb8a4c9af4a51529e14c4f00a9cce
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
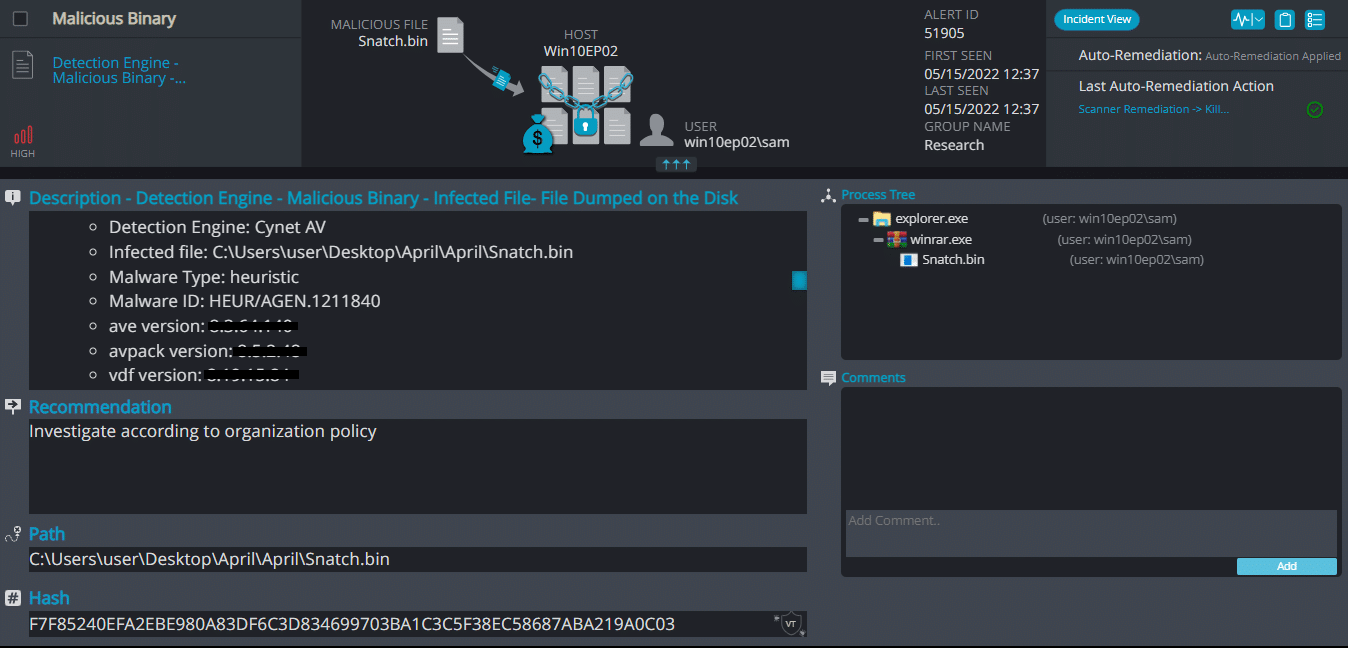
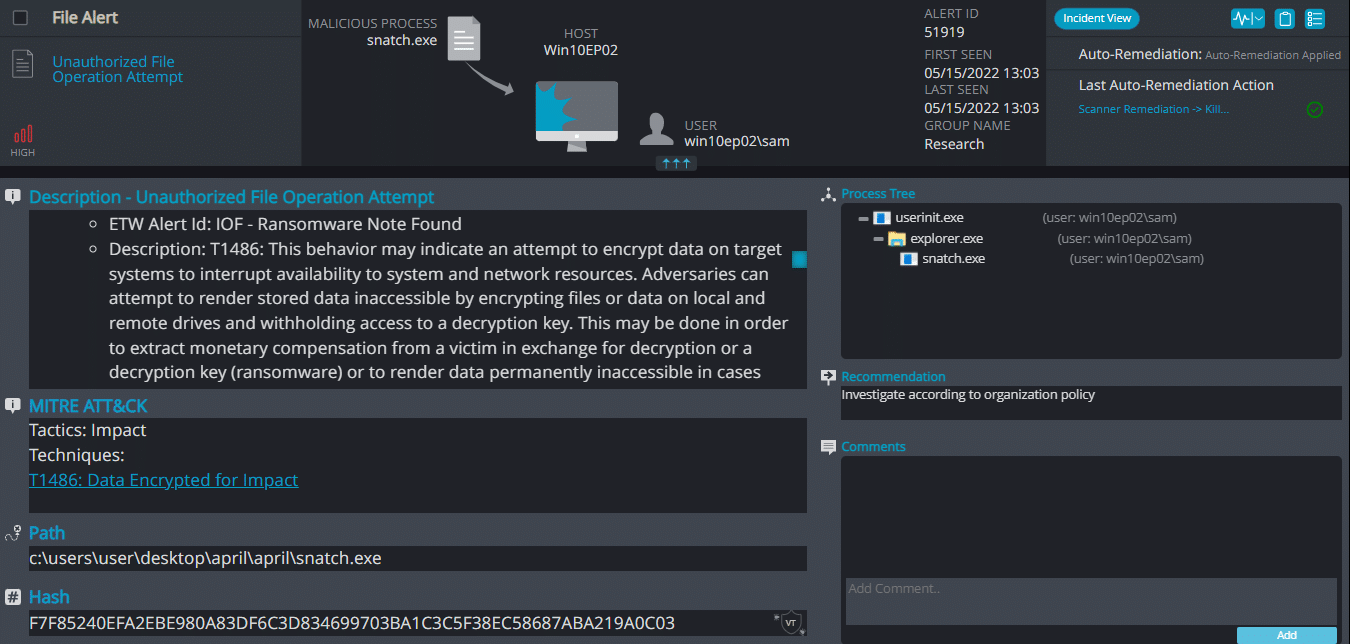
Snatch Overview
Snatch ransomware renames the encrypted files with .sdhvqq in the extension:

Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as HOW TO RESTORE YOUR FILES.TXT:

Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains instructions and the attacker’s contact info: