November 2022 Ransomware Activity Report
Written by: Maor Huli, Research Analyst
The ransomware from November to introduce are:
- CrySpheRe
- Inlock
- Anon_by
- Faust
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
As an integral department in Cynet’s research team, Orion works around the clock to track threat intelligence resources, analyze payloads, and automate labs to ensure that our customers are protected against the newest ransomware variants. In these monthly reports, Orion reviews the latest trends identified in Bleeping Computer — the most up-to-date website that summarizes the newest ransomware variants — and shares how Cynet detects these threats.
CYNET 360 AutoXDR™ VS RANSOMWARE
CrySpheRe Ransomware
- Observed since: Nov 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .CrySpheRe
- Ransomware note: КАК РАСШИФРОВАТЬ ФАЙЛЫ.txt
- Sample hash: 9680ddca296d16b58ceb381308e58509d73eafbf92d884b4a5865dcb843c0a63
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
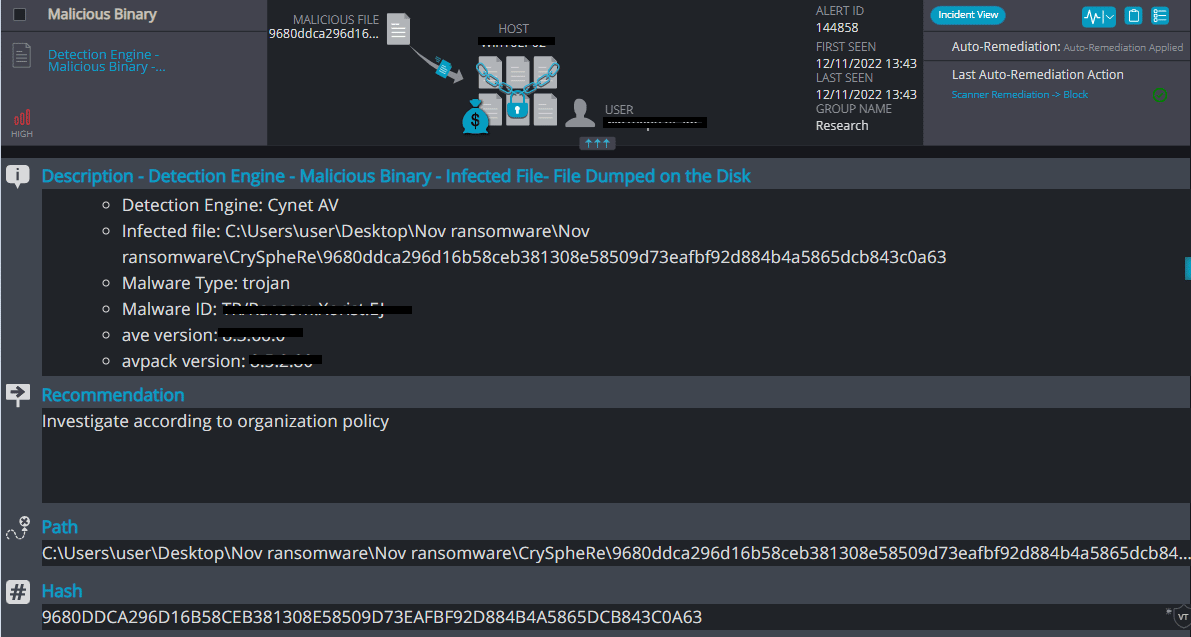
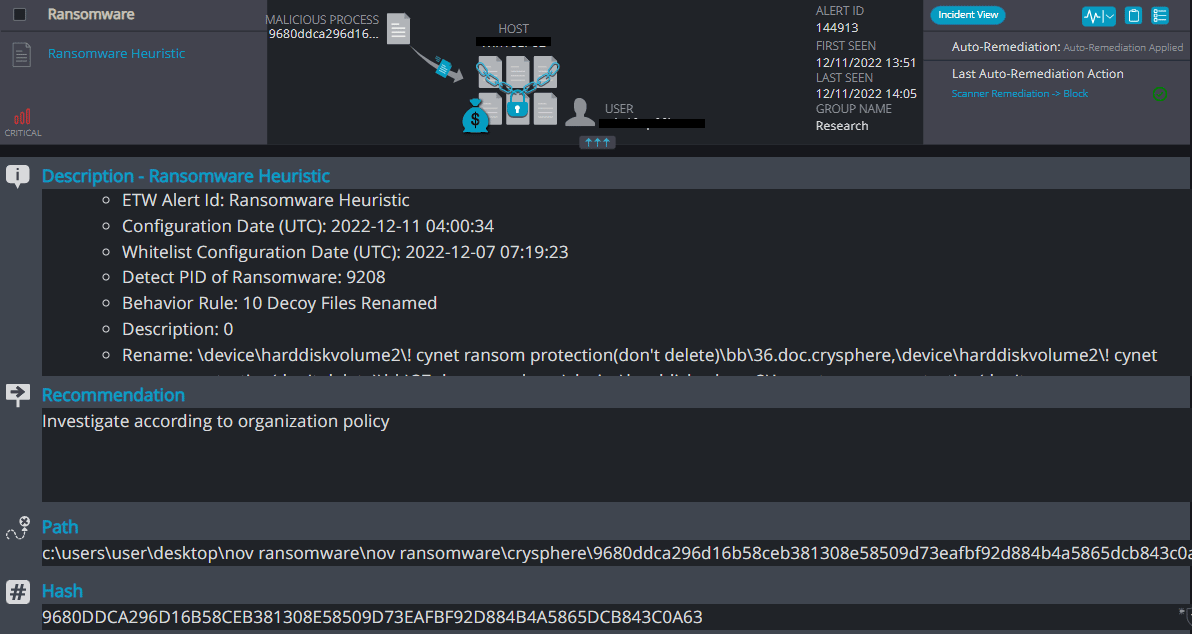
CrySpheRe Overview
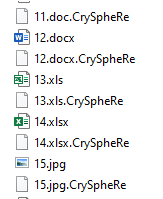
CrySpheRe ransomware renames the encrypted files with .CrySpheRe in the extension:
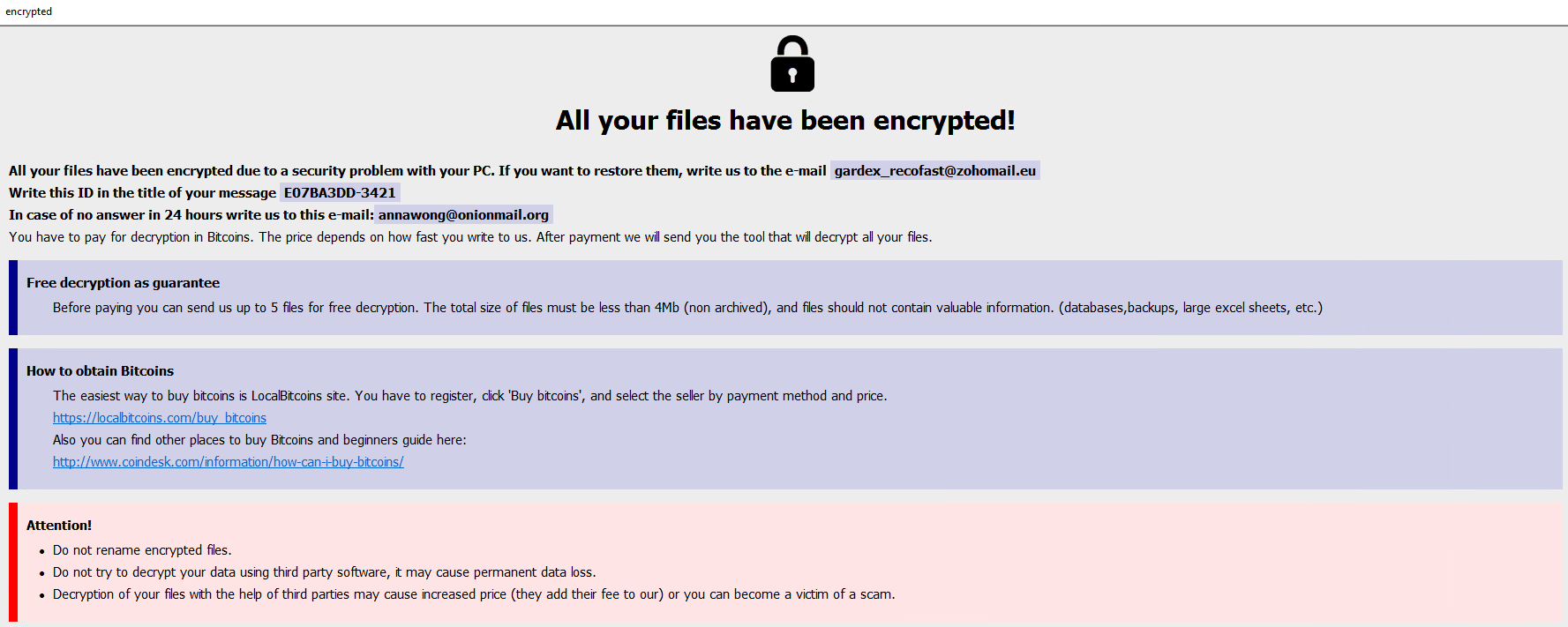
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as “КАК РАСШИФРОВАТЬ ФАЙЛЫ.txt”(No Russian Languange in the machine):

The ransomware note contains general information, warnings, and the attacker’s email address:
Inlock Ransomware
- Observed since: Nov 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .inlock
- Ransomware note: READ_IT.txt
- Sample hash: 96e48ea92e40ebe25e26aa769b38cbe27f26f2718d184a6ba2fd3bb900992ebd
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
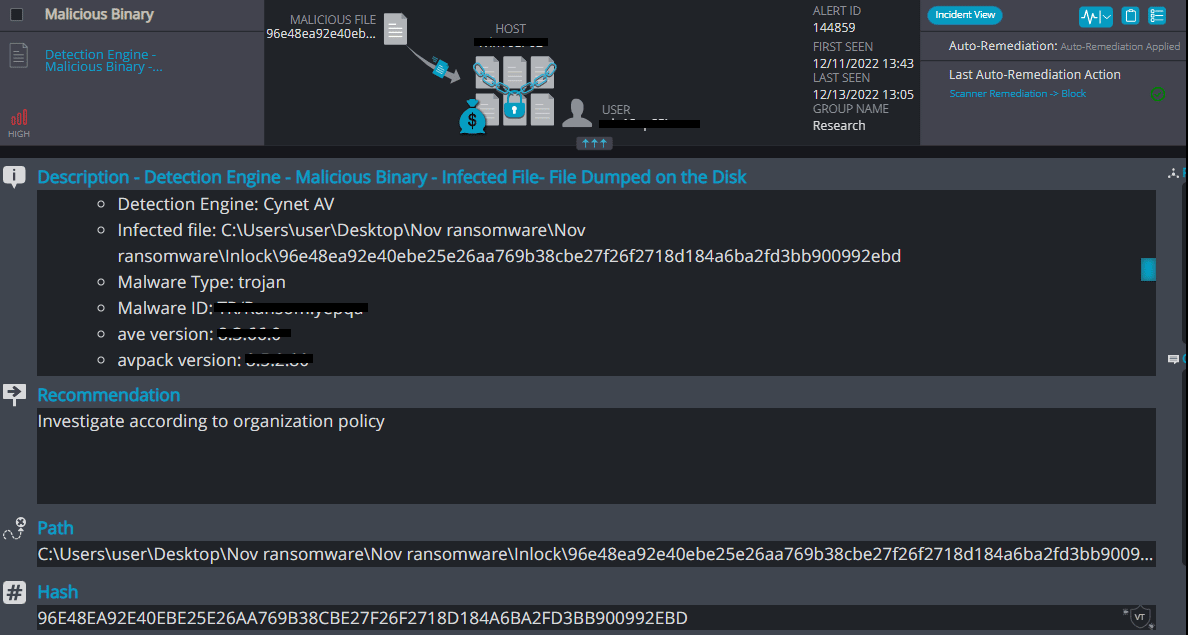
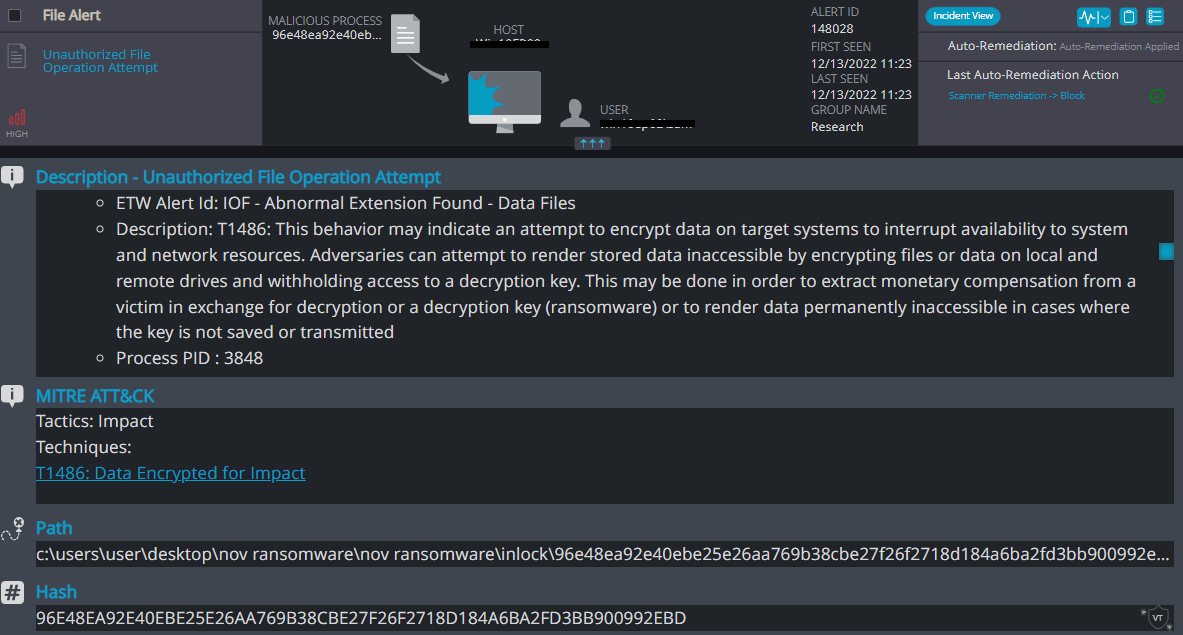
Inlock Overview
Inlock ransomware renames the encrypted files with .inlock in the extension:
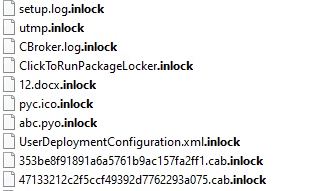
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note named “READ_IT.txt”:

The ransomware note contains general information and warnings, seemingly in Spanish:

After Translation:
The attacker says the decryption key will be sent once the payment arrives.

Anon_by Ransomware
- Observed since: Nov 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .anon_by
- Ransomware note: anon_by.txt
- Sample hash: 057824bbb1dca42df1af0cacde596f8a5d3bbf09a71bdbee5d2b48168b533e35
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
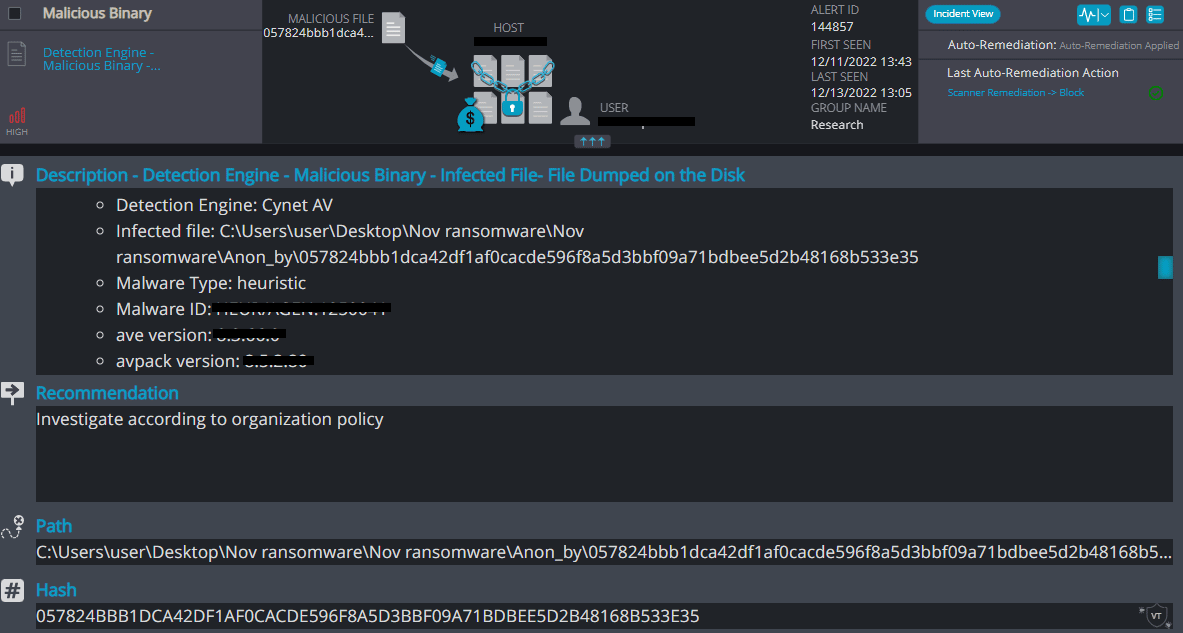
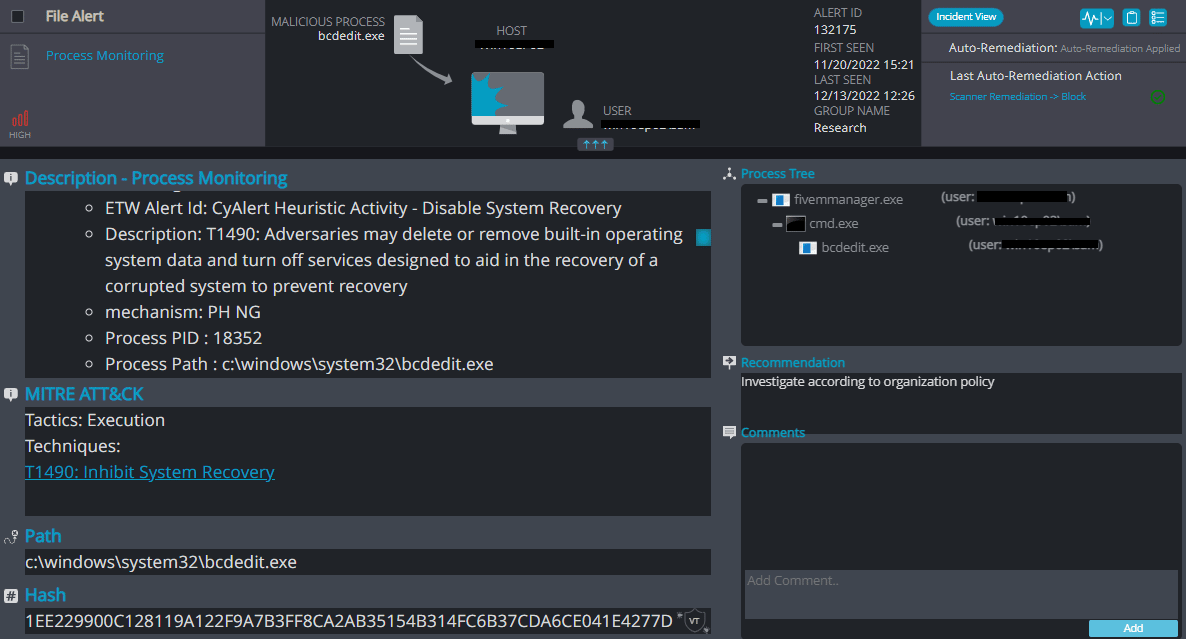
Anon_by Overview
Anon_by ransomware renames the encrypted files with .anon_by in the extension:
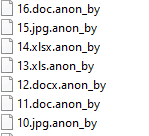
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note named “anon_by.txt”:

Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains vague general information, as well as the attacker’s tags:

Translated:

Faust Ransomware
- Observed since: Nov 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .faust
- Ransomware note: info.txt | .hta
- Sample hash: 0385dd2419adf0fe1a1e5d5ed28aaecbceb1411010fb06a1b0798d84eca4732e
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
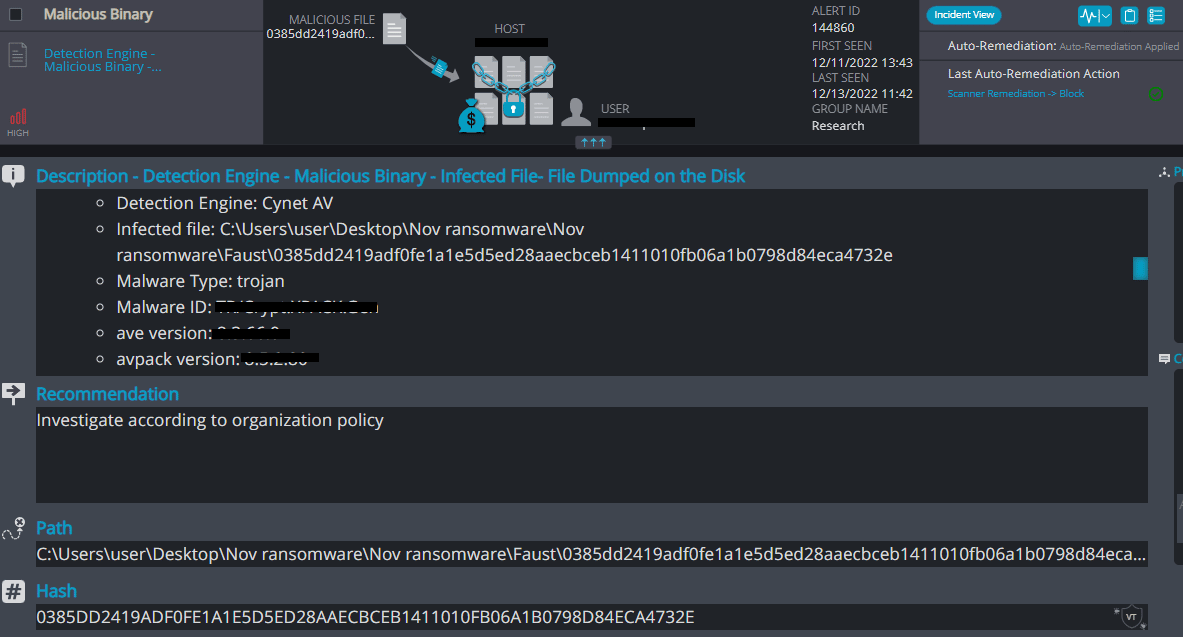
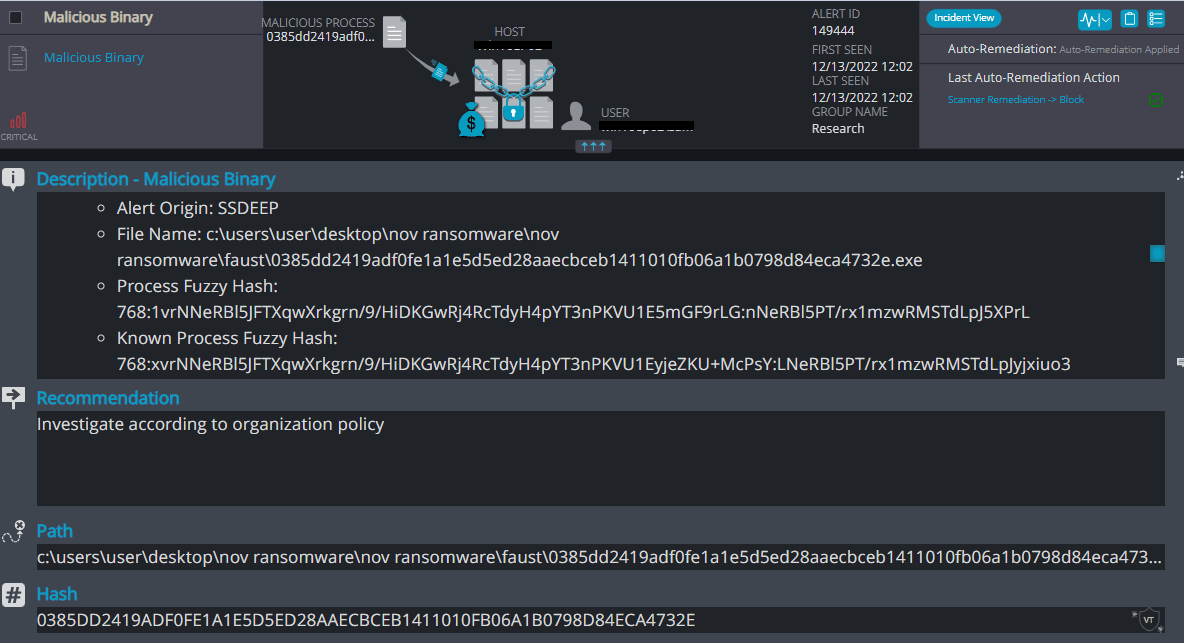
Faust Overview
Faust ransomware renames the encrypted files with the attacker’s contact email and .faust in the extension:
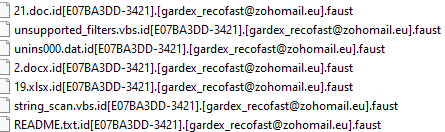
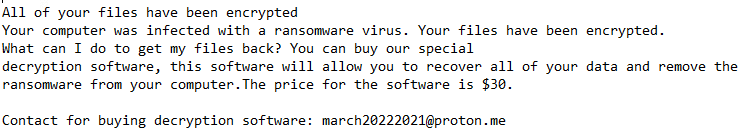
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note named “info.txt”:

And opens the note as a .hta file:

Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint. Then, after a while (approximately 15 minutes), it drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains general information and the attacker’s contact information:
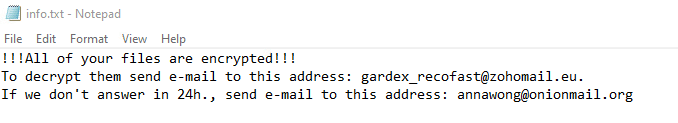
The hta file contains additional information, along with the general information in the text file. It also contains information on a free decryption option, how to buy bitcoins, and generic warnings: