Phishing Simulation: How It Works and 5 Tools to Get You Started
What Is a Phishing Simulation?
A phishing simulation is a cybersecurity training exercise where employees are subjected to fake phishing attacks in a controlled environment. These simulations aim to mimic real-world phishing attempts, helping employees recognize and respond to such threats.
By simulating various phishing scenarios, organizations can educate their workforce about the tactics used by cybercriminals, improving their ability to identify and avoid actual phishing attacks. The goal is to create a more security-aware culture and reduce the likelihood of successful phishing incidents.
Why Are Phishing Simulations Important?
Phishing simulations provide a practical, hands-on method for employees to learn how to detect phishing attempts. This practical experience is often more effective than theoretical training. The simulations also help identify vulnerable individuals or departments within an organization, allowing for targeted training and support.
Regular phishing simulations help keep cybersecurity awareness high, ensuring that employees remain vigilant and up-to-date with the latest phishing tactics. It can also identify gaps in defenses and help improve defensive measures. By reducing the success rate of phishing attacks, organizations can protect sensitive information, maintain regulatory compliance, and avoid the financial and reputational damage associated with data breaches.
Related content: Read our guide to anti phishing (coming soon)
How Do Phishing Simulations Work?
Phishing simulations typically follow a structured process:
- Designing the simulation: Cybersecurity teams or service providers create realistic phishing emails that mimic current tactics used by cybercriminals. These emails are designed to look legitimate, often replicating the appearance of common communications from trusted sources.
- Deploying the simulation: The simulated phishing emails are sent to employees without prior notice. This helps to assess the genuine reactions and awareness levels of the staff.
- Monitoring responses: The responses of employees to the phishing emails are monitored and recorded. This includes tracking who opens the email, clicks on links, or provides sensitive information.
- Providing feedback: Employees who fall for the simulated phishing attempts are provided with immediate feedback and educational resources. This helps them understand what they missed and how to avoid similar traps in the future.
- Analyzing results: The data collected from the simulation is analyzed to identify trends and areas needing improvement. This analysis can highlight hidden vulnerabilities and inform future training efforts.
- Iterative training: Based on the results, organizations can conduct follow-up simulations, targeting the identified weaknesses and ensuring continuous improvement in phishing awareness and response capabilities.
Tips From Expert
- Rotate phishing themes
Consistently update the themes of your simulations, not just the templates. Themes like fake HR updates, project requests, or unusual invoice alerts can catch even savvy users off guard. - Simulate multi-stage attacks
Advanced phishing tactics often involve multiple touchpoints, like an initial phishing email followed by a follow-up or phone call. Test your users’ response to multi-layered scenarios that resemble real-world attacks. - Integrate simulations with incident response drills
Enhance realism by embedding phishing simulations into broader incident response drills. This ensures employees practice not just avoiding phishing but also reporting and responding in a coordinated way. - Include real consequences for persistent failures
While simulations are educational, consider implementing consequences (like mandatory retraining or restricted access) for employees who repeatedly fall victim to simulated attacks. This reinforces the seriousness of phishing risks. - Correlate phishing data with broader threat landscape intelligence
Integrate the results from your phishing tests with threat intelligence feeds. This ensures your simulations evolve in line with the most current phishing tactics being observed in the wild.
What Is Phishing Simulation Software?
Phishing simulation software is a specialized tool designed to create and manage phishing simulations. This software enables organizations to launch realistic phishing attacks in a controlled environment, allowing employees to practice identifying and responding to these threats.
While it is possible to carry out phishing simulations manually, specialized software provides a more scalable and efficient way to conduct simulations on a regular basis. Manual simulations can be time-consuming and difficult to manage, especially in large organizations. Phishing simulation software automates many aspects of the process, from email creation to data analysis, making it easier to maintain regular training and track progress over time.
Phishing simulation solutions typically offer the following capabilities:
- Realistic cyber threats: Simulations aim to replicate various types of cybersecurity threats that mirror real-life scenarios. This allows employees to experience firsthand the tactics used by cybercriminals under controlled conditions. By exposing workers to such threats, they can learn to better recognize and avoid real attacks.
- Customizable phishing scenarios: Companies can tailor fake attacks to resemble those most likely to target their industry or department. This customization makes the simulations more relatable and engaging for employees, increasing the effectiveness of the training.
- Training program integration: Phishing simulation software often integrates seamlessly into broader cybersecurity training programs. This enables a holistic approach to learning, where employees can immediately practice the lessons learned from other training modules in realistic scenarios.
- Data-driven performance measurement: Data from simulation exercises allows organizations to measure the effectiveness of their cybersecurity training. These solutions often provide analytics on how individuals and groups perform during simulations, highlighting areas of strength and weakness across the workforce.
Notable Phishing Simulations and Testing Tools
Infosec IQ
Infosec IQ is a security awareness training and phishing simulation platform that aims to reduce cybersecurity incidents and reinforce secure behaviors across an organization. Its training content and automated features help organizations build a strong cybersecurity culture.
Features:
- Security awareness training: Offers industry- and role-based training that personalizes and contextualizes education for employees.
- Phishing simulations: Includes realistic phishing simulations that target employees’ inboxes.
- Automated training programs: Automates the delivery of training programs, making it easy to integrate with existing employee management and security tools.
- Reporting: Provides reporting features that help organizations track the success of their security training programs, identify high-risk areas, and prove compliance. Reports can be generated at the region, department, or employee level.
- Content library: Offers a large library of resources that is updated weekly. The content is mapped to nine core security behaviors outlined in the NIST security awareness and training guidelines.
Source: Infosec
2. Gophish
Gophish is an open-source phishing framework that helps assess an organization’s vulnerability to phishing attacks. It aims to be user-friendly and accessible, targeting organizations seeking to improve their phishing defenses without incurring significant costs.
Features:
- One-click installation: Can be installed quickly and easily with a single download.
- Full REST API: Powered by a REST API, which simplifies integration and automation. A Python client is available to enable API interactions.
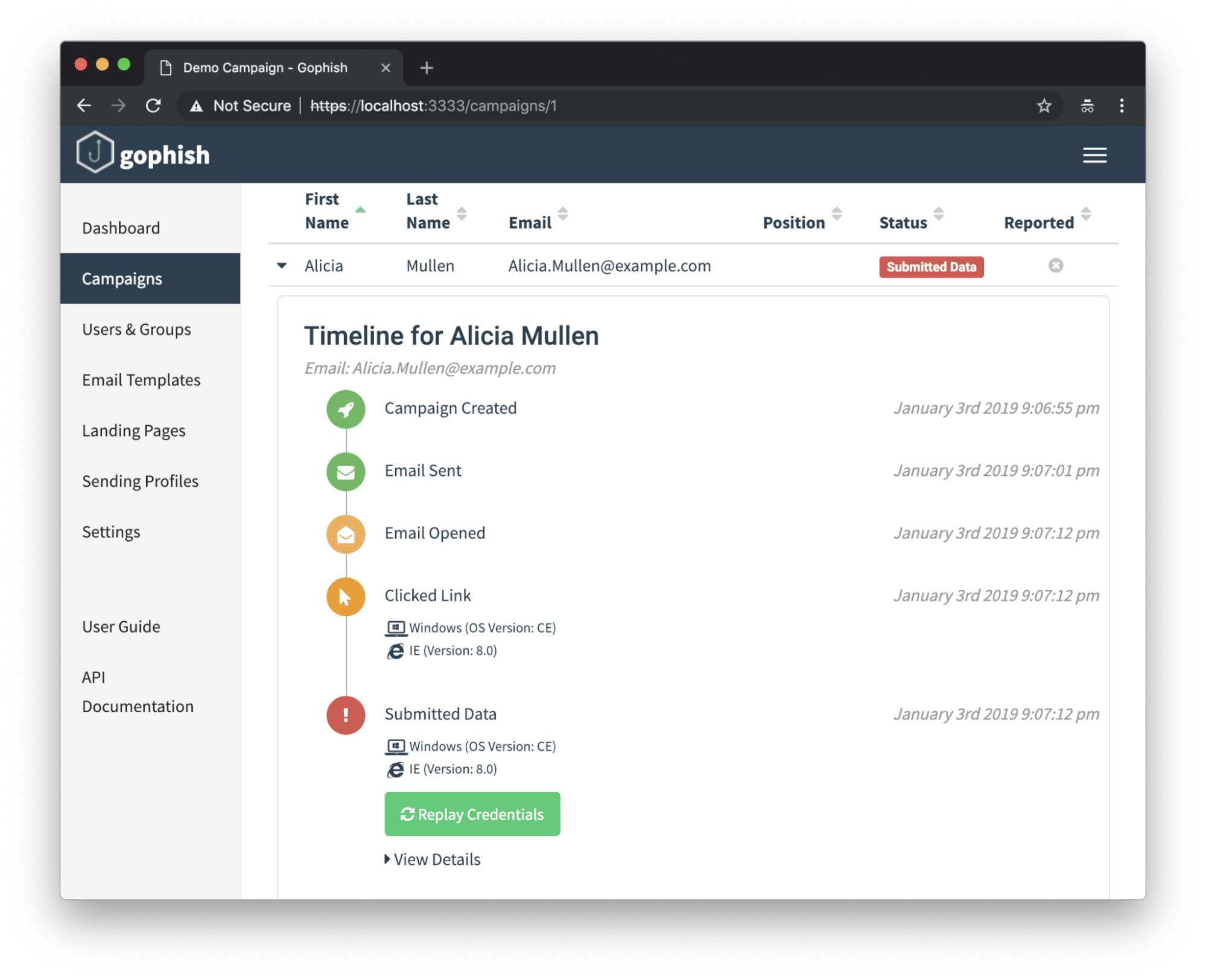
- Web UI: Includes an intuitive web interface that allows users to create or import phishing templates, track email opens, and manage campaigns.
- Cross-platform: Supports multiple platforms, including Windows, Mac OSX, and Linux, providing flexibility for diverse IT environments.
- Real-time results: Provides real-time updates, allowing users to monitor email opens, link clicks, and credential submissions as they happen.
3. Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET)
The Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET), created by Dave Kennedy, the founder of TrustedSec, is an open-source, Python-driven tool intended for social engineering penetration testing. Recognized and supported widely in the security community, SET is a useful resource for simulating advanced social engineering attacks to test organizational defenses.
Features:
- Social engineering attacks: Enables a range of social engineering attacks, using advanced techniques to mimic real-world scenarios. This helps organizations test their defenses against various social engineering threats.
- Open source and community support: With over two million downloads, SET is a widely used tool in the cybersecurity community. It is frequently updated and improved by contributions from users and experts.
- Conference recognition and endorsement: SET has been showcased at major cybersecurity conferences such as Blackhat, DerbyCon, Defcon, and ShmooCon.
- User-friendly interface: The Python-based architecture aims to simplify the use and integration of the toolkit into existing penetration testing frameworks.
4. ThriveDX Lucy
ThriveDX Lucy, formerly known as Lucy Security, is a phishing simulation and awareness training platform aimed at improving organizational security culture. It provides tools and training to help employees recognize and respond to cyber threats, reducing the risk of security breaches caused by human error.
Features:
- Attack tools: Offers attack simulations, including portable media, smishing, vishing, and whaling. A hacker toolkit allows for the creation of customized phishing campaigns.
- Customizable training and phishing awareness: Provides a catalog of over 1,000 customizable phishing templates and training content in more than 130 languages.
- Trusted technology and services: Supports flexible deployment options, including on-premises, cloud, and SCORM integration. It also ensures data security with strong encryption and offers managed services to aid in campaign setup and management.
- Dynamic reporting dashboard: Provides visibility into campaign performance and helps meet compliance requirements. This feature enables organizations to monitor and analyze the effectiveness of their training programs.
Source: ThriveDX
5. uPhish
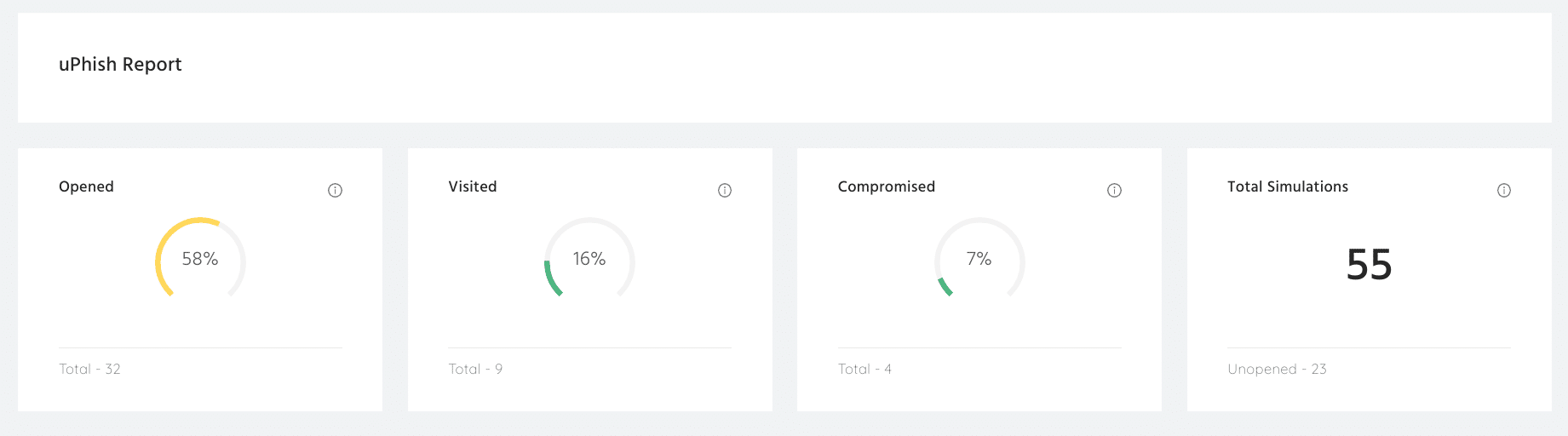
uPhish by usecure is a cloud-based phishing simulation platform used to identify and mitigate employee vulnerability to sophisticated phishing scams. It helps organizations improve their cybersecurity posture by building human resilience against phishing attacks.
Features:
- Fast setup: uPhish is fully cloud hosted, requiring no installations and offering a simple configuration process.
- Realistic templates: Includes a library of ready-made templates that impersonate trusted brands, making simulations as realistic as possible.
- AutoPhish: This feature automates regular phishing simulations to monitor user risk continuously, ensuring ongoing assessment and improvement.
- In-depth reporting: Provides reports on the performance of users, departments, and more, enabling analysis of vulnerabilities and training effectiveness.
- Spear-phishing: Runs targeted phishing tests by impersonating internal staff, helping to identify and address vulnerabilities within the organization.
- Follow-up training: Compromised users are automatically enrolled in follow-up training programs, ensuring they learn from their mistakes.
Source: usecure
Email Security with Cynet
Cynet Email Security is a holistic security solution that provides mail protection for Cloud Email Gateways. It combines a variety of capabilities including attachment and URL scanning to ensure your inbox stays safe, real-time link protection which allows scanning the original target in real-time each visit, attachment extension filtering to block risky attachments and avoid malware disguised as harmless files, and policy controls letting you block what’s bad and allow what’s trusted using customizable allowlists and blocklists.
Cynet Email Security provides the following capabilities:
- Automatically configure your Office365 gateway to be used with Cynet Email.
- Email attachment protection.
- Email link protection (including real-time checking of link targets when you open them).
- Tag emails that were sent from a domain that doesn’t match the administrator’s Office365 domain as External emails. You can also add domains that you consider “safe” and don’t need to be tagged as external.
- Create allowlists and blocklists for emails using the following parameters:
- Domain (URL)
- Sender email
- Recipient email
- File SHA256
In addition to email security, Cynet provides cutting edge capabilities:
- Advanced endpoint threat detection—full visibility and predicts how an attacker might operate, based on continuous monitoring of endpoints and behavioral analysis.
- Investigation and validation—search and review historic or current incident data on endpoints, investigate threats, and validate alerts. This allows you to confirm the threat before responding to it, reducing dwell-time and performing faster remediation.
- Rapid deployment and response—deploy across thousands of endpoints within two hours. You can then use it to perform automatic or manual remediation of threats on the endpoints, disrupt malicious activity and minimize damage caused by attacks.
Learn more about the Cynet All-in-One security platform.
Related Posts
Looking for a powerful, cost effective XDR solution?
- Full-Featured XDR, EDR, and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response