Top 6 EDR Tools Compared [2025 Update]

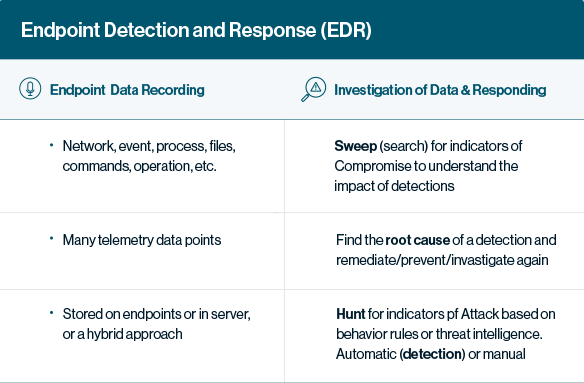
EDR is a cybersecurity technology that continuously monitors devices to detect and respond to cyber threats like ransomware and malware. EDR solutions gather and analyze information related to security threats, like ransomware and malware, on computer workstations and other endpoints, making it possible to identify security breaches as they happen and facilitate a quick response. This makes EDRs a staple product in any security stack.
In this blog post, we dive deep into how EDRs work and compare the six leading EDR tools and EDR vendors in the market: Cynet, Trellix, Symantec, SentinelOne, CrowdStrike, and Cybereason. After reading this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge that can help you find the right EDR solution for your own needs.
How Do EDR Work?
EDR solutions continuously ingest data from endpoints, including event logs, running applications, and authentication attempts. Here is how the process usually works.
Gathering Data – Collecting telemetry data from endpoints and sending it to the EDR platform.
Analyzing Data – Using ML to correlate and analyze data, creating a baseline of normal behavior and ongoing flagging of suspicious activity.
Responding – Predefined triggers that automate responses to threats.
For example, temporarily isolating an endpoint to block malware from spreading across the network. Data is retained for future investigations.
Related content: Read our guide to EDR RFP template
EDR Security Capabilities
Automated Response
EDR solutions can provide automated responses to threats on endpoints.
This includes actions such as quarantining infected files, blocking malicious network connections, or even completely isolating an affected endpoint from the network. Automation allows security teams to focus on investigating and resolving the issue without having to worry about containment.
Analysis and Forensics
EDR tools help security teams perform rapid analysis and forensics on detected threats. They provide valuable insights into the nature of the threat, including its origin, how it operates, and how it can be mitigated. Over time, EDR tools can provide a historical log of events for advanced analysis and strategy development.
Threat Intelligence
EDR solutions integrate with threat intelligence feeds, improving their ability to accurately identify malicious activity.
Threat Hunting
Actively searching for signs of compromise or suspicious activity within an organization’s network that may not have been detected by automated mechanisms.
Threat hunting can identify stealthy and persistent threats such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and insider threats that can evade traditional security measures. In addition, security vendors can provide managed threat hunting services carried out by their experienced security experts.
Real-Time and Historical Visibility
EDR solutions provide both real-time and historical visibility into endpoint activity. Real-time visibility enables security teams to react quickly to potential threats, minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers. Historical visibility can support forensic investigations and help identify patterns or trends that may indicate a larger security issue.
Multiple Response Options
EDR tools provide a range of response options to detected threats.
These response options allow organizations to choose the most appropriate action based on the specific nature of each threat and their unique security requirements.
What are EDR Tools?
EDR tools are technology platforms that can alert security teams of malicious activity, and enable fast investigation and containment of attacks on endpoints. An endpoint can be an employee workstation or laptop, a server, a cloud system, a mobile or IoT device.
EDR solutions typically aggregate data on endpoints including process execution, endpoint communication, and user logins; analyze data to discover anomalies and malicious activity; and record data about malicious activity, enabling security teams to investigate and respond to incidents. In addition, they enable automated and manual actions to contain threats on the endpoint, such as isolating it from the network or wiping and reimaging the device.
Related content: Read our guide to EDR vs SIEM.
6 Notable EDR Tools
Below is a quick review of our top 6 endpoint protection tools that include an EDR component: Trellix, Symantec, RSA, CrowdStrike, Cybereason, and our own Cynet Security Platform. For each vendor we explain the context of the EDR module within the broader security solution, and list EDR features as described by the vendors.
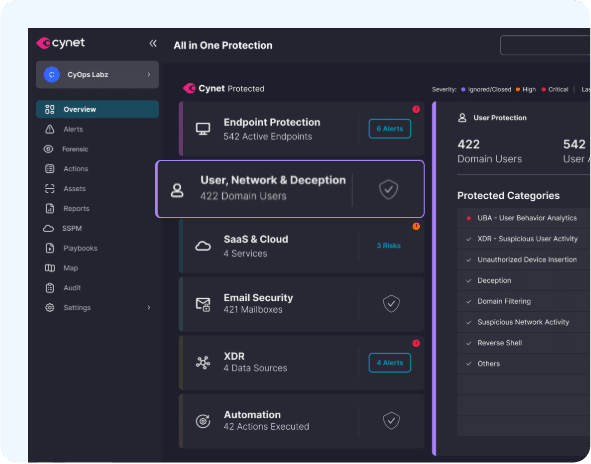
Cynet All-in-One Cybersecurity Platform
Solution scope:
The Cynet All-In-One Cybersecurity Platform is an integrated security solution that goes beyond endpoint protection, offering NGAV, EDR, UEBA, deception, network monitoring and protection.
Delivery model:
On prem, Cloud or hybrid
Product page:
https://www.cynet.com/platform/
Source: Cynet
Cynet EDR Features:
- Correlation—leverages the integrated security platform, provides visibility into network traffic and user activity, together with endpoint-specific activity
- Validation—correlation of all activity signals enables strict validation on any suspicious behavior, reducing false positive
- Alert—provides full context for rapid and efficient triage, prioritization and onward steps on a single screen
- Deep investigation—instant access to data from all endpoints, with granular search filters to go beyond the local detected event and view all related malicious activity
- Remediation—enables control at the host, file and process level—from complete host isolation to surgical actions like scheduled task deletion
- Automation—enables custom remediation workflows that are applied automatically when a similar incident recurs
- Threat hunting—provides validated IOCs remediation actions, enabling analysis to hunt for threats across the environment and uncover hidden attack instances
Pricing:
Cynet offers organizations two main types of packages:
- Elite – XDR platform with 24X7 MDR support, at $7/month/endpoint.
- All-in-One – Full enterprise security platform with 24X7 MDR support, at $10/month/endpoint.
Both packages include platform management, advanced EPP, EDR, UBA, NDR, Response Orchestration, and Deception. The Elite package includes optional MDT, SSPM, and CSPM, log management and open XDR, and MDR services.
The enterprise package includes everything in the elite package, including all optional services, as well as ESPM and email security.
Verdict:
A full endpoint and network protection solution that is easy to use. Offers robust protection validated by MITRE. Good for SMEs and MSPs.
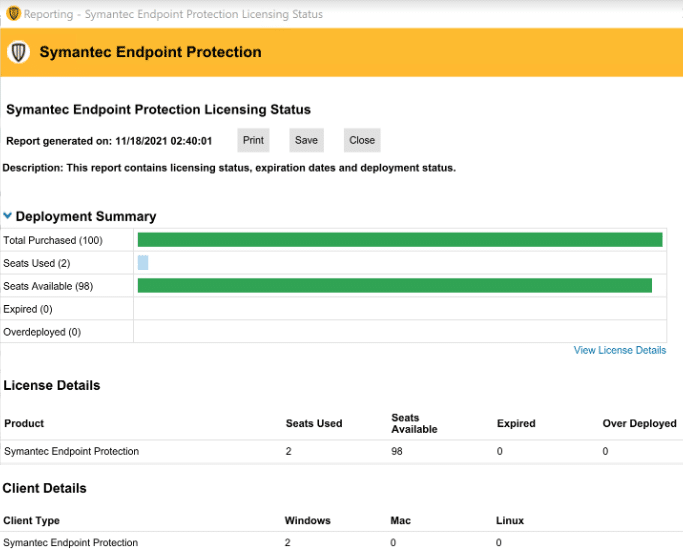
Symantec Endpoint Protection
Solution scope:
Symantec Endpoint Protection offers an endpoint security that covers all major devices and operating systems, integrating various protection technologies to address the full attack chain.
Delivery model:
Virtual or physical appliance
Product page:
https://www.symantec.com/products/endpoint-protection
Source: Broadcom
EDR Features:
- Threat Detection and Response—Monitors for suspicious endpoint activity and detects threats across attack vectors.
- Automated Response Actions—Quickly isolates compromised endpoints and prevents lateral movement to minimize potential damage.
- Sophisticated Attack Analytics—Analyzes threats using AI-guided detection methods, helping SOC teams prioritize critical incidents.
- Integrated Threat Intelligence—Leverages Symantec’s Global Intelligence Network to identify known attack tactics, techniques, and procedures.
- Scalable Management—A single-agent architecture ensures flexible deployment options (on-premises, cloud, or hybrid).
- Post-Incident Forensics and Reporting—Provides detailed threat analysis and incident logs to support post-attack investigations and compliance.
Pricing:
Symantec was acquired by Broadcom and is offered for purchase through Broadcom’s extensive network of authorized distributors, value-added resellers (VARs), and global partners. As a result, pricing is not listed publicly and can vary significantly depending on the region, the specific product suite, licensing terms, and any enterprise agreements or bundles negotiated through the local Broadcom partner.
Verdict:
Built for complex IT environments and offers an advanced threat intelligence network. As a Broadcom tool, it is best for Broadcom fans. Plus, there’s the question of the competition with Broadcom’s Carbon Black (both tools became a part of Broadcom through acquisitions).
SentinelOne’s Singularity XDR
SentinelOne offers Singularity XDR, which is based on its EDR solution. Singularity XDR ingests and correlates data across endpoints, the cloud, and identities and provides custom and automated detection and response.
Delivery Model:
Cloud-native and agentless.
Product page:
https://www.sentinelone.com/platform/how-singularity-xdr-works/
Source: SentineOne
XDR Features:
Here’s a bulleted list of key features from the SentinelOne Singularity™ XDR platform, as described on the official page:
- Unified Data Lake – Collects, correlates, and stores telemetry from across endpoints, cloud, and identity systems.
- Automated Threat Mitigation – Performs one-click or automatic remediation, including rollback of ransomware.
- Storyline™ Technology – Automatically tracks and visualizes threat activity in real time, creating context-rich incident timelines.
- Storyline Active Response (STAR) – Enables custom detection and response rules.
- AI-Powered Detection and Response – Uses machine learning to identify known and unknown threats quickly and accurately.
- Singularity Marketplace Integrations – Provides out-of-the-box integrations with a wide range of third-party security tools.
Pricing:
XDR capabilities are available as part of the Control Package, at $79.99/endpoint, and for higher-tier packages as well.
Verdict:
SentinelOne is a good choice for enterprises with multiple data sources that need assistance with visibility and analysis. It’s recommended for hands-on security teams who like to “get their hands dirty” building rules, diving into integrations, etc.
CrowdStrike Falcon Insight
Solution scope:
Falcon Insight is an EDR module as part of the Falcon Endpoint Protection Enterprise solution, which also includes NGAV, threat intelligence, USB device protection, and threat hunting.
Delivery model:
Cloud
Product page:
https://www.crowdstrike.com/endpoint-security-products/falcon-endpoint-protection-enterprise/
Source: Crowdstrike
EDR Features:
- Automatically uncovers stealthy attackers—applies behavioral analytics to detect traces of suspicious behavior.
- Integrates with threat intelligence—faster detection of the activities, tactics, techniques and procedures identified as malicious
- Real-time and historical visibility—hundreds of security-related events such as process creation, drivers loading, registry modifications, disk access, memory access, network
- Fast remediation and real-time response—isolates an endpoint under attack from the network; provides built-in remote execution commands including deleting a fill, killing a process, running a script, restart/shutdown
- Information collectors—enable analysts to explore file systems, list running processes, retrieve Windows event lots, extract process memory, collect environment variables, etc.
- Remediation actions—nable teams to take action to contain or remediate a threat with speed and decisiveness.
Pricing:
Falcon Insight XDR is part of CrowdStrike’s Enterprise and Complete Bundles.
- Enterprise: $184.99 per device per year. Includes AV, USB device control, firewall control, threat hunting and intelligence, and XDR.
- Complete: Bespoke pricing and bespoke bundles
Verdict:
CrowdStrike provides the enterprise with advanced security, visibility, and monitoring. However, CrowdStrike is considered complicated to deploy, and it has limited support for legacy systems. Plus, teams report many false positives.
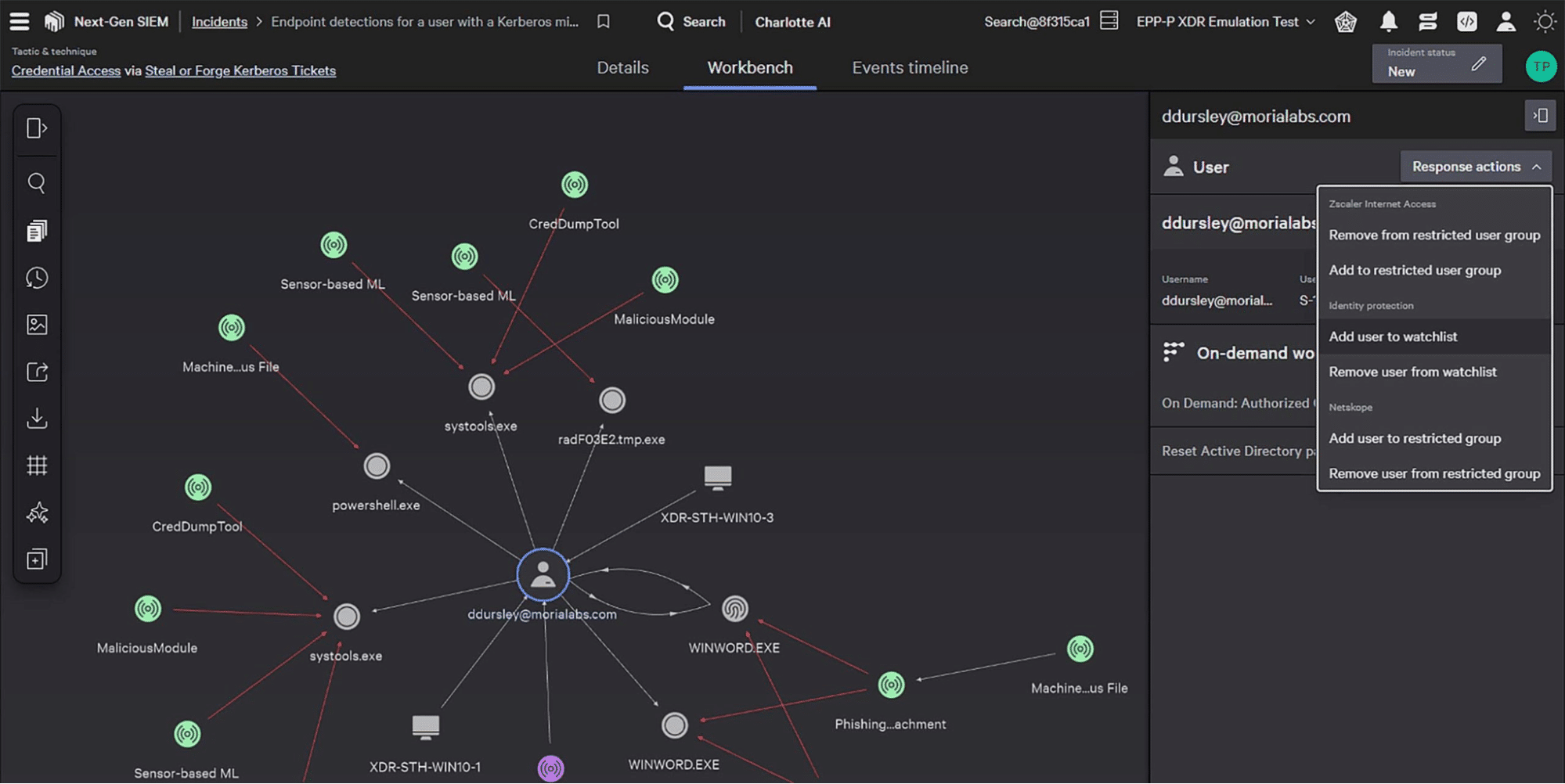
Cybereason Endpoint Detection and Response
Solution scope:
A module within the Cybereason Defense Platform, which also includes NGAV and Managed Detection and Response (MDR).
Source: Cybereason
EDR Features:
- Threat examination—shows entire process tree, timeline, and all malicious activity across machines for each process
- Third party alerts—combines EDR data with alerts from firewall and SIEM tools
- Attack full scope—see all related attack elements, including root cause, affected machines and users, incoming and outgoing communications, attack timeline
- Customization—custom rules and behavioral whitelisting
- Guided remediation—execute commands from a complete remediation toolbox on the endpoint, enables access to remote shell
- Enterprise-wide remediation—responds to threats affecting many machines, by executing remediation actions on all affected machines in one step
Pricing:
CyberReason offers three types of bundles to enterprises, all including EDR. However, prices aren’t listed.
Verdict:
CyberReason is considered a solid security tool. However, users report some friction points in user experience, support, and automation capabilities. Built for enterprises.
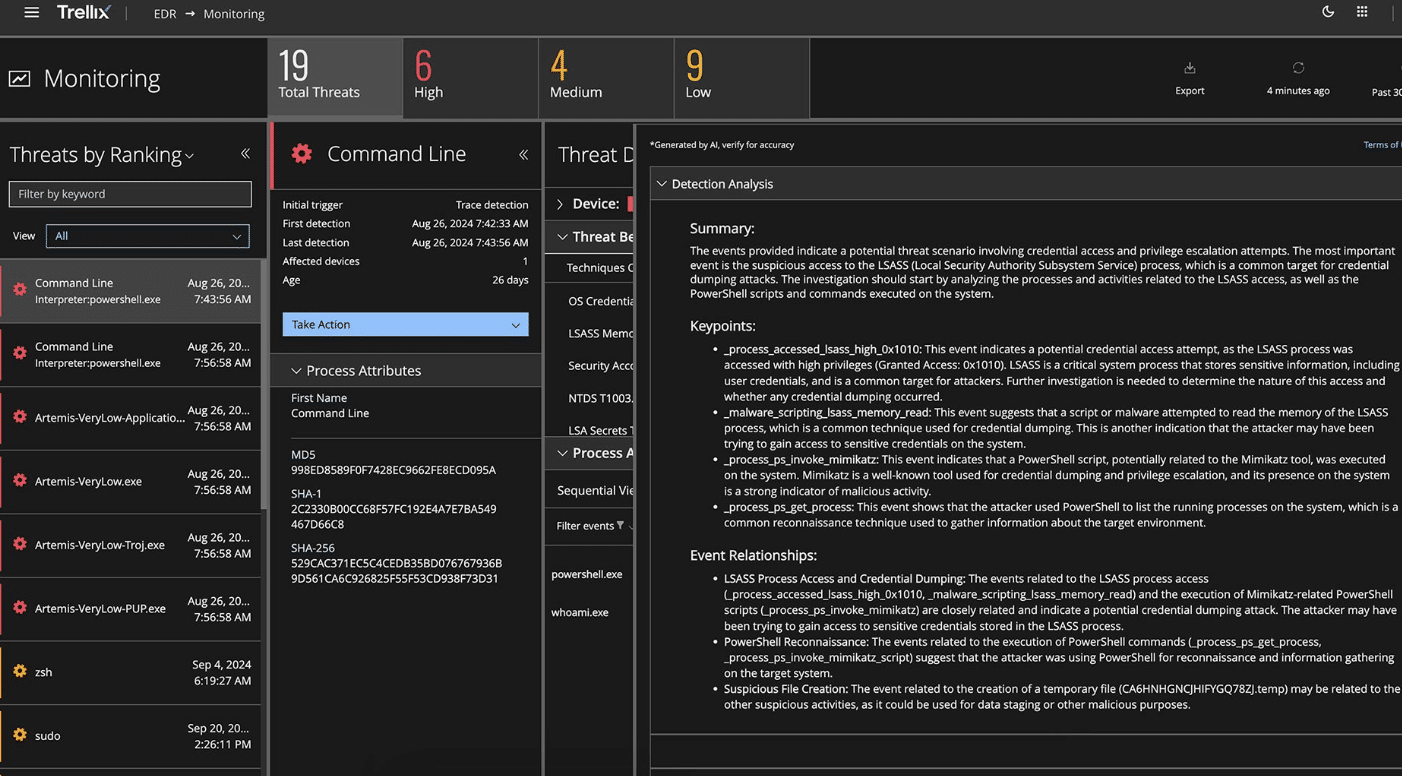
Trellix
Solution scope:
- Threat analysis
- Threat detection, based on analysis and connection of disparate events
- Mapping to MITRE ATT&CK
- Forensics to capture and store files, memory, process, and disk images
Delivery model:
Appliance or cloud
Source: Trellix
Pricing:
Trellix EDR is available on the AWS marketplace and ranges from $50-$150/user per year, depending on the package.
Verdict:
Trellix acquired FireEye’s EDR to create a robust security solution fit for the enterprise. As happens with these acquisitions, deployment and use are considered complex and full of friction, so prepare your IT team.
Tips From Expert
- Leverage AI and Machine Learning for Enhanced Threat Detection: Choose EDR solutions that utilize AI and machine learning to detect and respond to threats. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, establish baselines for normal behavior, and identify subtle anomalies that might indicate advanced or stealthy attacks, improving overall detection accuracy.
- Customize Automated Response Actions to Align with Your Organization’s Security Policies: Tailor automated response actions to align with your organization’s specific security policies and risk tolerance. For example, you can configure your EDR to automatically isolate high-risk endpoints upon detection of certain types of malware, while alerting administrators for further investigation in lower-risk scenarios.
- Implement Continuous Threat Hunting for Proactive Threat Discovery: Use your EDR’s threat hunting capabilities to proactively search for potential threats that may have bypassed automated detection mechanisms. Regular threat hunting can help uncover hidden adversaries and reduce the dwell time of attackers in your network.
- Integrate EDR with Existing Security Infrastructure for Comprehensive Threat Visibility: Ensure that your EDR solution integrates seamlessly with your existing security tools such as SIEM, firewalls, and vulnerability management systems. This integration allows for better data correlation and more comprehensive threat visibility, enabling faster and more informed responses.
- Regularly Update and Test Endpoint Agents for Optimal Performance: Ensure that the EDR agents installed on endpoints are regularly updated to maintain compatibility with the latest threat signatures and detection capabilities. Additionally, periodically test the agents’ functionality to confirm they are properly collecting and transmitting data.
See Additional Guides on Key Data Security Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of data security.
Incident Response
Authored by Cynet
- What Is Incident Response? Strategy, Process, Templates & More
- What Is a SOC? 10 Core Functions and 6 Key Challenges
- Incident Response Team: A Blueprint for Success
Object Storage
Authored by Cloudian
- What is Object Storage: Definition, How It Works and Use Cases
- Object Storage vs. File Storage: What’s the Difference?
- How Object Storage Protects You From Ransomware
Penetration Testing
Authored by HackerOne
EDR Tools Questions and Answers
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a security category defined by Gartner in 2013. It is intended to fill security gaps on endpoint devices like employee workstations, servers, and mobile devices. EDR helps security teams investigate and immediately respond to malicious activities at remote endpoints to contain and mitigate attacks.
EDR continuously monitors endpoints for suspicious behavior. This helps security teams detect and investigate incidents in real time, including attacks that perimeter security tools could not detect. In case of malicious activity, EDR tools can help trace the source, contain the threat, and remediate the damage.
Traditional antivirus software relies mostly on signature-based detection. It can catch known threats but often misses new or evolving ones. EDR, on the other hand, is behavior-based. It looks at how processes behave, how files interact, and how users move through systems. This allows it to detect anomalies or suspicious activity even if the specific malware hasn’t been seen before.
When evaluating EDR solutions, look for solutions that offer end-to-end threat detection and response by correlating network, user, and endpoint activity. This will allow them to validate suspicious behavior and reduce false positives. In addition, opt for tools that allow deep investigation across endpoints and flexible and automated remediation options. And don’t underestimate ease of use. If the UI is clunky, response time (and IT) will suffer.
EDR provides visibility and control at the endpoint level, where many attacks begin. Rather than relying solely on perimeter defenses, EDR detects threats that have already bypassed traditional defenses. This reduces dwell time and helps prevent full-scale breaches.
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and others require organizations to demonstrate they have robust security controls in place. EDR tools help meet these requirements by providing detailed logs, forensic data, and reporting capabilities that show how threats are detected and managed. Additionally, EDR supports compliance by enabling rapid incident response and breach containment, which are often required in regulatory mandates.
EDR tools are designed to work as part of a broader security ecosystem. Most integrate with SIEM systems to provide deeper insights and centralized logging and with SOAR platforms to trigger automated workflows in response to detected threats. Additionally, many EDR solutions can share data with threat intelligence platforms, firewall logs, IAM tools, and even XDR or MDR platforms for a wider context. This interoperability allows security teams to correlate data across systems, enabling faster investigations and more informed decision-making.
EDR systems deploy agents on end-user devices, which are used to continuously monitor activity and network traffic to and from the device. These events are recorded in a central database. EDR tools analyze the data to identify incidents, investigate them, and use the data to find similar threats on other endpoints across the organization.
Most importantly, EDR allows security teams to immediately see what is happening on the endpoint and take action to contain and eradicate threats.
Learn more in our detailed guide to EDR vs Antivirus.
Antivirus software can stop threats based on malware, but is not effective against other types of threats. It also cannot protect against malware that evades detection. EDR is able to detect and respond to threats that evade antivirus and other traditional defenses on the endpoint device.
EDR solutions, on their own, do not replace antivirus. EDR is typically part of an endpoint protection platform (EPP), which includes advanced antivirus and anti-malware protection. EDR works together with antivirus – it relies on antivirus to stop some threats, but is able to detect and respond to threats that were not captured by antivirus software.
Related content: Read our guide to EPP vs. EDR
Related Posts
Looking for a powerful, cost effective XDR solution?
- Full-Featured XDR, EDR, and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response