SIEM Cyber Security Capabilities, 4 Common Challenges & Solutions
What Is SIEM?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. SIEM software collects and aggregates log data generated throughout the organization’s technology infrastructure, from host systems and applications to network and security devices such as firewalls and antivirus filters.
SIEM solutions are critical for comprehensive threat detection, as they centralize the security data collected from various sources, allowing for faster identification, analysis, and response to potential security events. By integrating outputs from multiple products, SIEMs provide a unified approach to understanding and managing threats, enhancing the security posture of an organization.
Why Is SIEM Important for Cyber Security?
Threat Detection and Prevention
SIEMs play an essential role in threat detection by constantly monitoring data for signs of unusual activity that could indicate a security threat. This continuous monitoring ensures that all events are analyzed, providing security teams with the ability to detect malicious activity early and mitigate potential threats promptly.
SIEM’s sophisticated analytics tools and integrated threat intelligence helps organizations detect advanced threats and prioritize security events based on their potential impact.
Incident Response Efficiency
With SIEM, organizations can dramatically improve the efficiency of their incident response activities. The centralized dashboard provided by SIEM systems offers immediate insights, supporting quick decision-making during a critical security event. This results in a more coordinated and timely response, reducing potential damages.
Additionally, SIEMs automate much of the incident response process by pre-establishing workflows and response scenarios. This automation ensures that all team members are aware of their tasks and can operate quickly and within a structured framework.
Regulatory Compliance
SIEM solutions also ease the burden of compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. By consolidating and securing logs of all network and application activity, SIEMs create a clear, immutable trail of evidence that can be analyzed to ensure compliance with various standards and provide the data necessary for internal and external audits.
Most SIEMs are also equipped with features specifically designed to assist with compliance management, such as predefined reports for common regulatory requirements. These tools significantly reduce the time and effort required to prepare for audits by automatically generating necessary documentation and reports.
Key Cybersecurity Capabilities of SIEM Solutions
Here are the primary cybersecurity features and capabilities SIEM solutions provide.
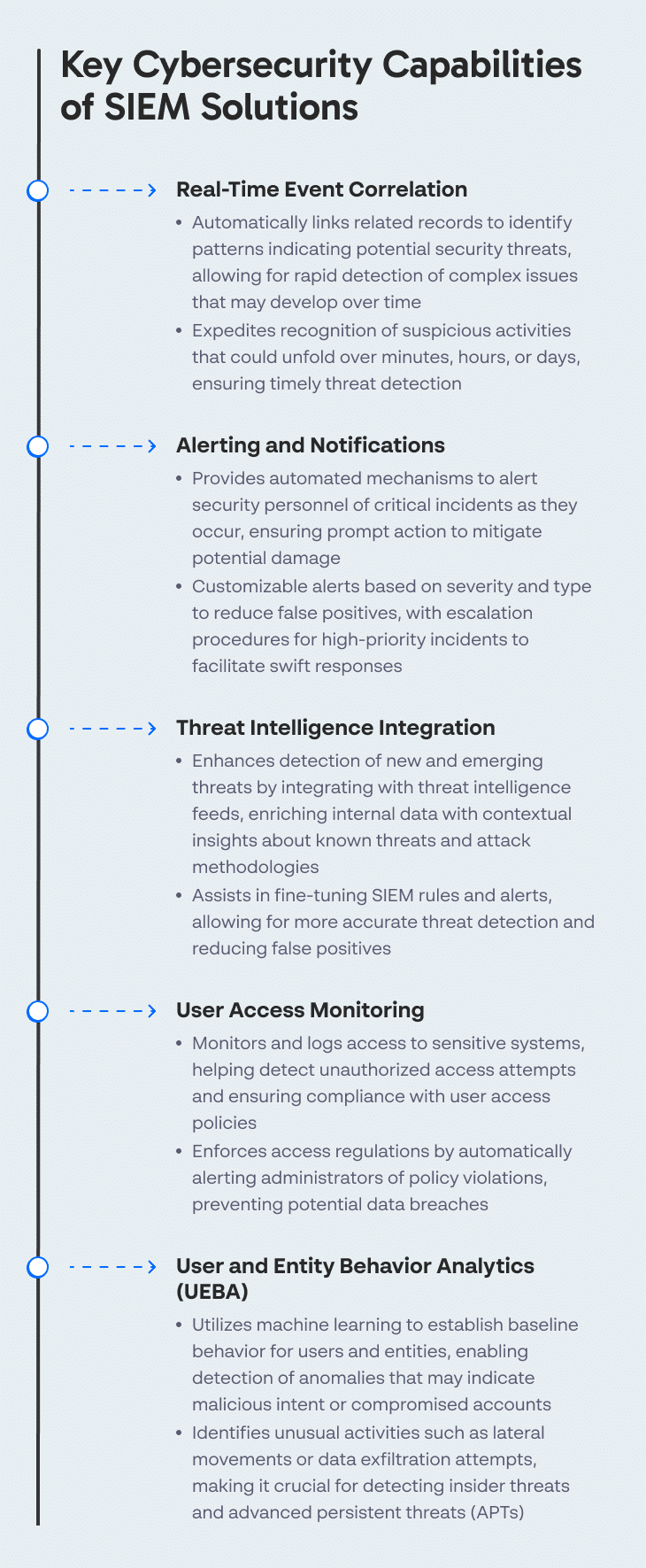
Real-Time Event Correlation
One of the most impactful features of SIEM systems is real-time event correlation, which automatically links related records to identify patterns that may indicate a security threat. This capability allows security teams to quickly detect complex threats that are not identifiable through a single event or log entry.
Real-time correlation expedites the detection of suspicious activities that could unfold over minutes, hours, or days, ensuring threats are recognized as soon as they develop.
Alerting and Notifications
SIEM systems provide automated alerting and notification mechanisms to inform security personnel of critical incidents as they occur. This feature ensures that potential threats are promptly addressed before they can cause significant damage. Alerts can be customized based on severity, type, or other criteria to ensure that they capture truly threatening activities without overwhelming the staff with false positives.
SIEMs can also escalate alerts automatically to ensure that high-priority security incidents are communicated to the right personnel or management without delay. This improves the speed and efficiency of response efforts.
Threat Intelligence Integration
Integration with threat intelligence feeds is another crucial feature of SIEM systems, enhancing the detection of new and emerging threats. These feeds provide contextual data about known bad actors, vulnerabilities, and attack methodologies, enriching the internal data with external threat intelligence. This integration helps organizations stay ahead of attackers.
Threat intelligence feeds also assist in fine-tuning SIEM rules and alerts based on the latest threat landscape, allowing for more accurate threat detection and fewer false positives. This proactive approach provides organizations with a dynamic defense posture, significantly enhancing their ability to counter sophisticated cyber threats.
User Access Monitoring
SIEM systems enhance security by monitoring and controlling access to sensitive systems and information. They track and log all access events, which helps organizations detect unauthorized attempts to gain access to critical resources. Monitoring privileged users is particularly important as these accounts can alter system settings or access sensitive data, making them a prime target for attackers.
In addition to access monitoring, SIEMs can enforce user access policies and regulations, automatically alerting administrators of policy violations. This tight control over user activities helps prevent data breaches and ensures that all users comply with the organization’s security policies.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA is a feature within advanced SIEM systems that utilizes machine learning and statistical models to establish baseline normal behavior for users and entities within the network. By continuously comparing new behavior against this baseline, UEBA can identify activities that deviate from the norm, potentially indicating malicious intent or a compromised account.
Additionally, UEBA can detect anomalies in data access and usage that traditional security tools might overlook, such as lateral movements or data exfiltration attempts by already authenticated users. This capability makes UEBA a vital component in the detection of insider threats and advanced persistent threats (APTs), where unauthorized activities blend in with regular operations.
Tips From Expert
1. Tailor SIEM Deployment to Your Environment:
Customize your SIEM to align with your unique network architecture, application landscape, and business processes. This ensures the system monitors the most relevant data sources and provides actionable insights.
2. Integrate with Endpoint and Network Security Tools:
Enhance your SIEM’s capabilities by integrating it with EDR and NDR tools. This provides a more comprehensive view of threats across all layers of your IT infrastructure, improving detection accuracy.
3. Regularly Update and Tune Correlation Rules:
Keep your SIEM’s correlation rules up-to-date by refining them based on new threat intelligence and past incident data. This ongoing tuning helps reduce false positives and ensures the SIEM adapts to emerging threats.
4. Leverage Machine Learning for Advanced Threat Detection:
Incorporate machine learning algorithms within your SIEM to improve anomaly detection and reduce false positives. Machine learning can identify patterns and behaviors that traditional rule-based systems might miss.
5. Implement Role-Based Access Controls:
Enforce strict RBAC within your SIEM to ensure only authorized personnel can view, modify, or respond to security alerts. This minimizes the risk of insider threats and protects sensitive security data.
SIEM Security Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While SIEM is a critical component of most security stacks, it also raises challenges for security teams. Here are the primary challenges and how your organization can address them.
1. Noise in Event Data
SIEM platforms typically process vast amounts of log data, which can lead to significant noise, i.e., large volumes of non-threat-related data that obscure actual security threats. This noise complicates the threat detection process, potentially causing critical warnings to be overlooked among false positives.
Overcoming the challenge:
- Implement advanced filtering: Apply more refined filtering rules to discard irrelevant or redundant log entries before they are processed. This approach reduces the volume of data to analyze, making it easier to spot genuine threats.
- Leverage machine learning: Utilize machine learning algorithms to better identify patterns and anomalies within the data, which can help distinguish between normal activities and potential security threats. This can increase the accuracy of threat detection and reduce false positives.
2. Blind Spots in Data Sources
SIEM’s effectiveness depends on the comprehensiveness of the data it analyzes. Blind spots in data collection can occur if certain network segments, systems, or applications are not adequately covered by the SIEM’s data collection framework. This may arise due to technical limitations, architectural complexities, or oversight in the deployment phase.
Overcoming the challenge:
- Comprehensive integration: Ensure all potential data sources are integrated into the SIEM system, including cloud services, remote endpoints, and third-party applications. This creates a more complete view of the security landscape.
- Regular audits and updates: Conduct regular audits to identify any new or previously overlooked data sources. Keep the SIEM configuration updated to include these sources to maintain visibility across the entire network.
3. Ineffective Correlation Rules
In SIEM systems, correlation rules determine how different events are linked to detect multi-stage attacks and subtle anomalies. However, if these rules are not well defined or maintained, they may either fail to detect actual threats or generate an overwhelming number of false positives. This could lead to crucial alerts being ignored or valuable resources wasted on investigating non-issues.
Overcoming the challenge:
- Continuous rule optimization: Regularly review and update correlation rules to adapt to the evolving threat landscape and organizational changes. This includes removing outdated rules and adjusting others to improve accuracy.
- Customize rules based on context: Develop context-aware correlation rules that take into account the specific environment, such as the type of business, typical network traffic patterns, and known safe behaviors.
4. Alert Fatigue
Alert fatigue occurs when security teams are overwhelmed by a high volume of alerts, many of which may be false positives. This can lead to slower response times, overlooked alerts, and increased risk of missing actual threats. Constant exposure to large numbers of alerts can desensitize staff to notifications, reducing their attentiveness and effectiveness.
Overcoming the challenge:
- Prioritize and classify alerts: Implement a tiered alert system that classifies alerts by severity and potential impact. This allows teams to focus on the most critical issues first, reducing the cognitive load and improving response times.
- Enhance alert management with automation: Use automation to handle low-priority alerts and routine tasks, freeing up security personnel to concentrate on more complex and serious threats. Automated response protocols can also help mitigate threats faster.
Overcoming SIEM Challenges by Integrating XDR
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions can significantly enhance SIEM capabilities by providing a more holistic approach to threat detection and response. By integrating XDR, organizations can consolidate data from various security products into a single platform, offering a unified view that helps identify and respond to sophisticated attacks more efficiently.
XDR’s ability to correlate data across different security layers—endpoint, network, cloud, and applications—complements SIEM’s log management capabilities, providing deeper insights and more accurate threat detection.
XDR systems often include more advanced analytical tools and machine learning capabilities than traditional SIEM solutions. These features can help reduce false positives and enhance threat detection by learning from security events and adapting over time. In addition, integrating XDR with SIEM can alleviate alert fatigue by leveraging XDR’s ability to filter out irrelevant data and prioritize threats based on their severity and impact.
Security Automation with Cynet
Cynet provides the world’s first Autonomous Breach Protection platform that natively integrates endpoint, network and user attack prevention/detection of XDR with log management and analysis of CLM and automated investigation and remediation capabilities of SOAR, backed by a 24/7 world-class MDR service.
End to end, fully automated breach protection is now within reach of any organization, regardless of security team size and skill level. Most smaller businesses find that Centralized Log Management (CLM) is fully sufficient for their needs while far more affordable and usable than SIEM solutions.
XDR Layer: End-to-End Prevention & Detection
- Endpoint protection—multilayered protection against malware, ransomware, exploits and fileless attacks.
- Network protection—protecting against scanning attacks, MITM, lateral movement and data exfiltration.
- User protection—preset behavior rules coupled with dynamic behavior profiling to detect malicious anomalies.
- Deception—wide array of network, user, file decoys to lure advanced attackers into revealing their hidden presence.
CLM Layer: Log Management and Analysis
- Ingest log data—collect all pertinent log data to uncover threats across your environment
- Data visualization—advanced, targeted data queries pinpoint precursors to cyberattacks and perform forensic analysis
- Threat hunting—uncover evidence of compromised endpoints, systems, and data such as anomalous privileged account activity and anomalous outbound traffic
- Regulatory compliance—generate reports for FISMA, GLBA, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI DSS, for example, that regulatory bodies require.
SOAR Layer: Response Automation
- Investigation—automated root cause and impact analysis.
- Findings—actionable conclusions on the attack’s origin and its affected entities.
- Remediation—elimination of malicious presence, activity and infrastructure across user, network and endpoint attacks.
- Visualization—intuitive flow layout of the attack and the automated response flow.
MDR Layer: Expert Monitoring and Oversight
- Alert monitoring—First line of defense against incoming alerts, prioritizing and notifying customers on critical events.
- Attack investigation—Detailed analysis reports on the attacks that targeted the customer.
- Proactive threat hunting—Search for malicious artifacts and IoC within the customer’s environment.
- Incident response guidance—Remote assistance in isolation and removal of malicious infrastructure, presence and activity.
Simple Deployment
Cynet can be deployed across thousands of endpoints in less than two hours. It can be immediately used to uncover advanced threats and then perform automatic or manual remediation, disrupt malicious activity and minimize damage caused by attacks.
Get a free trial of Cynet and experience the world’s only integrated XDR, CLM, SOAR and MDR solution.
Related Posts
Looking for a powerful, cost effective XDR solution?
- Full-Featured XDR, EDR, and NGAV
- Anti-Ransomware & Threat Hunting
- 24×7 Managed Detection and Response